---
comments: true
---
# Image Feature Module Tutorial
## I. Overview
The image feature module is one of the important tasks in computer vision, primarily referring to the automatic extraction of useful features from image data using deep learning methods, to facilitate subsequent image retrieval tasks. The performance of this module directly affects the accuracy and efficiency of the subsequent tasks. In practical applications, image features typically output a set of feature vectors, which can effectively represent the content, structure, texture, and other information of the image, and will be passed as input to the subsequent retrieval module for processing.
## II. Supported Model List
> The inference time only includes the model inference time and does not include the time for pre- or post-processing.
| Model | Model Download Link |
Recall@1 (%) |
GPU Inference Time (ms)
[Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
CPU Inference Time (ms)
[Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
Model Storage Size (MB) |
Description |
| PP-ShiTuV2_rec |
Inference Model/Training Model |
84.2 |
3.91 / 1.06 |
6.82 / 2.89 |
16.3 |
PP-ShiTuV2 is a general image feature system consisting of three modules: object detection, feature extraction, and vector retrieval. These models are part of the feature extraction module and can be selected based on system requirements. |
| PP-ShiTuV2_rec_CLIP_vit_base |
Inference Model/Training Model |
88.69 |
12.57 / 11.62 |
67.09 / 67.09 |
306.6 |
| PP-ShiTuV2_rec_CLIP_vit_large |
Inference Model/Training Model |
91.03 |
49.85 / 49.85 |
229.14 / 229.14 |
1050 |
Test Environment Description:
- Performance Test Environment
- Test Dataset:PaddleX Custom Dataset.
- Hardware Configuration:
- GPU: NVIDIA Tesla T4
- CPU: Intel Xeon Gold 6271C @ 2.60GHz
- Software Environment:
- Ubuntu 20.04 / CUDA 11.8 / cuDNN 8.9 / TensorRT 8.6.1.6
- paddlepaddle 3.0.0 / paddlex 3.0.3
Inference Mode Description
| Mode |
GPU Configuration |
CPU Configuration |
Acceleration Technology Combination |
| Normal Mode |
FP32 Precision / No TRT Acceleration |
FP32 Precision / 8 Threads |
PaddleInference |
| High-Performance Mode |
Optimal combination of pre-selected precision types and acceleration strategies |
FP32 Precision / 8 Threads |
Pre-selected optimal backend (Paddle/OpenVINO/TRT, etc.) |
## III. Quick Integration
> ❗ Before quick integration, please install the PaddleX wheel package. For detailed instructions, refer to the [PaddleX Local Installation Guide](../../../installation/installation.en.md)
After installing the wheel package, a few lines of code can complete the inference of the image feature module. You can switch between models under this module freely, and you can also integrate the model inference of the image feature module into your project. Before running the following code, please download the [demo image](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/general_image_recognition_001.jpg) to your local machine.
```python
from paddlex import create_model
model_name = "PP-ShiTuV2_rec"
model = create_model(model_name)
output = model.predict("general_image_recognition_001.jpg", batch_size=1)
for res in output:
res.print()
res.save_to_json("./output/res.json")
```
After running, the result is:
```bash
{'res': {'input_path': 'general_image_recognition_001.jpg', 'page_index': None, 'feature': array([ 0.04910231, ..., -0.07126085], dtype=float32)}}
```
The meanings of the parameters are as follows:
- `input_path`: The path to the input image to be predicted.
- `feature`: The extracted image feature vector, with a dimensionality equal to the model's output feature dimension, which is 512 in this case.
Descriptions of related methods, parameters, etc., are as follows:
* The `create_model` method instantiates an image feature model (using `PP-ShiTuV2_rec` as an example). Specific descriptions are as follows:
| Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Options |
Default Value |
model_name |
The name of the model |
str |
None |
None |
model_dir |
The storage path of the model |
str |
None |
None |
device |
The device used for model inference |
str |
It supports specifying specific GPU card numbers, such as "gpu:0", other hardware card numbers, such as "npu:0", or CPU, such as "cpu". |
gpu:0 |
use_hpip |
Whether to enable the high-performance inference plugin |
bool |
None |
False |
hpi_config |
High-performance inference configuration |
dict | None |
None |
None |
* The `model_name` must be specified. When `model_name` is specified, PaddleX's built-in model parameters are used by default. If `model_dir` is specified, the user-defined model is used.
* The `predict()` method of the image feature model is called for inference. The parameters of the `predict()` method are `input` and `batch_size`, with specific descriptions as follows:
| Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Options |
Default Value |
input |
Data to be predicted, supporting multiple input types |
Python Var/str/list |
- Python Variable, such as image data represented by
numpy.ndarray
- File Path, such as the local path of an image file:
/root/data/img.jpg
- URL Link, such as the web URL of an image file: Example
- Local Directory, the directory should contain the data files to be predicted, such as the local path:
/root/data/
- List, the elements of the list should be of the above-mentioned data types, such as
[numpy.ndarray, numpy.ndarray], [\"/root/data/img1.jpg\", \"/root/data/img2.jpg\"], [\"/root/data1\", \"/root/data2\"]
|
None |
batch_size |
Batch size |
int |
Any integer |
1 |
* Process the prediction results. Each sample's prediction result is of type `dict`, and supports operations such as printing, saving as an image, and saving as a `json` file:
| Method |
Description |
Parameter |
Type |
Explanation |
Default Value |
print() |
Print the result to the terminal |
format_json |
bool |
Whether to format the output content with JSON indentation |
True |
indent |
int |
Specify the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable. Only effective when format_json is True |
4 |
ensure_ascii |
bool |
Control whether non-ASCII characters are escaped to Unicode. When set to True, all non-ASCII characters will be escaped; False retains the original characters. Only effective when format_json is True |
False |
save_to_json() |
Save the result as a json file |
save_path |
str |
The file path for saving. When a directory is provided, the saved file name matches the input file name |
None |
indent |
int |
Specify the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable. Only effective when format_json is True |
4 |
ensure_ascii |
bool |
Control whether non-ASCII characters are escaped to Unicode. When set to True, all non-ASCII characters will be escaped; False retains the original characters. Only effective when format_json is True |
False |
* Additionally, the prediction results can be accessed via properties, as follows:
| Property |
Description |
json |
Get the prediction result in json format |
For more information on using PaddleX's single-model inference APIs, refer to the [PaddleX Single Model Python Script Usage Instructions](../../instructions/model_python_API.en.md).
## IV. Custom Development
If you seek higher accuracy from existing models, you can leverage PaddleX's custom development capabilities to develop better image feature models. Before developing image feature models with PaddleX, ensure you have installed the classification-related model training plugins for PaddleX. The installation process can be found in the [PaddleX Local Installation Guide](../../../installation/installation.en.md)
### 4.1 Data Preparation
Before model training, you need to prepare the corresponding dataset for the task module. PaddleX provides data validation functionality for each module, and only data that passes validation can be used for model training. Additionally, PaddleX provides demo datasets for each module, which you can use to complete subsequent development. If you wish to use private datasets for model training, refer to [PaddleX Image Feature Task Module Data Annotation Tutorial](../../../data_annotations/cv_modules/image_feature.en.md).
#### 4.1.1 Demo Data Download
You can use the following commands to download the demo dataset to a specified folder:
```bash
wget https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/data/Inshop_examples.tar -P ./dataset
tar -xf ./dataset/Inshop_examples.tar -C ./dataset/
```
#### 4.1.2 Data Validation
A single command can complete data validation:
```bash
python main.py -c paddlex/configs/modules/image_feature/PP-ShiTuV2_rec.yaml \
-o Global.mode=check_dataset \
-o Global.dataset_dir=./dataset/Inshop_examples
```
After executing the above command, PaddleX will validate the dataset and summarize its basic information. If the command runs successfully, it will print `Check dataset passed !` in the log. The validation results file is saved in `./output/check_dataset_result.json`, and related outputs are saved in the `./output/check_dataset` directory in the current directory, including visual examples of sample images and sample distribution histograms.
👉 Details of Validation Results (Click to Expand)
The specific content of the validation result file is:
"done_flag": true,
"check_pass": true,
"attributes": {
"train_samples": 1000,
"train_sample_paths": [
"check_dataset/demo_img/05_1_front.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/02_1_front.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/02_3_back.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/04_3_back.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/04_2_side.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/12_1_front.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/07_2_side.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/04_7_additional.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/04_4_full.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/01_1_front.jpg"
],
"gallery_samples": 110,
"gallery_sample_paths": [
"check_dataset/demo_img/06_2_side.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/01_4_full.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/04_7_additional.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/02_1_front.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/02_3_back.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/02_3_back.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/02_4_full.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/03_4_full.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/02_2_side.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/03_2_side.jpg"
],
"query_samples": 125,
"query_sample_paths": [
"check_dataset/demo_img/08_7_additional.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/01_7_additional.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/02_4_full.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/04_4_full.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/09_7_additional.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/04_3_back.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/02_1_front.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/06_2_side.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/02_7_additional.jpg",
"check_dataset/demo_img/02_2_side.jpg"
]
},
"analysis": {
"histogram": "check_dataset/histogram.png"
},
"dataset_path": "./dataset/Inshop_examples",
"show_type": "image",
"dataset_type": "ShiTuRecDataset"
}
In the above validation results, check_pass being True indicates that the dataset format meets the requirements. Explanations for other indicators are as follows:
* attributes.train_samples: The number of training samples in this dataset is 1000;
* attributes.gallery_samples: The number of gallery (or reference) samples in this dataset is 110;
* attributes.query_samples: The number of query samples in this dataset is 125;
* attributes.train_sample_paths: A list of relative paths to the visual images of training samples in this dataset;
* attributes.gallery_sample_paths: A list of relative paths to the visual images of gallery (or reference) samples in this dataset;
* attributes.query_sample_paths: A list of relative paths to the visual images of query samples in this dataset;
Additionally, the dataset verification also analyzes the number of images and image categories within the dataset, and generates a distribution histogram (histogram.png):
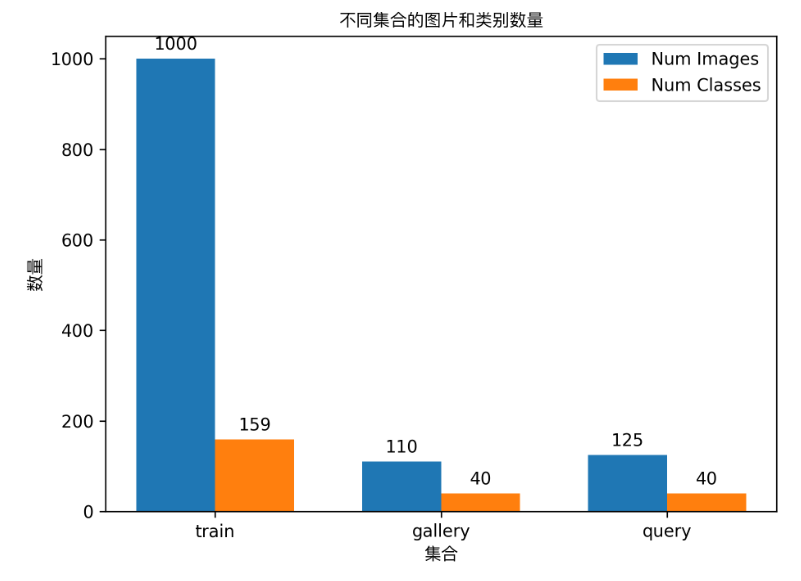
👉 Details of Format Conversion / Dataset Splitting (Click to Expand)
(1) Dataset Format Conversion
The image feature task supports converting LabelMe format datasets to ShiTuRecDataset format. The parameters for dataset format conversion can be set by modifying the fields under CheckDataset in the configuration file. Some example parameter descriptions in the configuration file are as follows:
CheckDataset:convert:enable: Whether to perform dataset format conversion. The image feature task supports converting LabelMe format datasets to ShiTuRecDataset format, default is False;src_dataset_type: If dataset format conversion is performed, the source dataset format needs to be set, default is null, optional value is LabelMe;
For example, if you want to convert a LabelMe format dataset to ShiTuRecDataset format, you need to modify the configuration file as follows:
cd /path/to/paddlex
wget https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/data/image_classification_labelme_examples.tar -P ./dataset
tar -xf ./dataset/image_classification_labelme_examples.tar -C ./dataset/
......
CheckDataset:
......
convert:
enable: True
src_dataset_type: LabelMe
......
Then execute the command:
python main.py -c paddlex/configs/modules/image_feature/PP-ShiTuV2_rec.yaml \
-o Global.mode=check_dataset \
-o Global.dataset_dir=./dataset/image_classification_labelme_examples
After the data conversion is executed, the original annotation files will be renamed to xxx.bak in the original path.
The above parameters also support being set by appending command line arguments:
python main.py -c paddlex/configs/modules/image_feature/PP-ShiTuV2_rec.yaml \
-o Global.mode=check_dataset \
-o Global.dataset_dir=./dataset/image_classification_labelme_examples \
-o CheckDataset.convert.enable=True \
-o CheckDataset.convert.src_dataset_type=LabelMe
(2) Dataset Splitting
The parameters for dataset splitting can be set by modifying the fields under CheckDataset in the configuration file. Some example parameter descriptions in the configuration file are as follows:
CheckDataset:split:enable: Whether to re-split the dataset. When True, the dataset will be re-split, default is False;train_percent: If the dataset is re-split, the percentage of the training set needs to be set, the type is any integer between 0-100, and it needs to ensure that the sum of gallery_percent and query_percent values is 100;
For example, if you want to re-split the dataset with 70% training set, 20% gallery set, and 10% query set, you need to modify the configuration file as follows:
......
CheckDataset:
......
split:
enable: True
train_percent: 70
gallery_percent: 20
query_percent: 10
......
Then execute the command:
python main.py -c paddlex/configs/modules/image_feature/PP-ShiTuV2_rec.yaml \
-o Global.mode=check_dataset \
-o Global.dataset_dir=./dataset/Inshop_examples
After the data splitting is executed, the original annotation files will be renamed to xxx.bak in the original path.
The above parameters also support being set by appending command line arguments:
python main.py -c paddlex/configs/modules/image_feature/PP-ShiTuV2_rec.yaml \
-o Global.mode=check_dataset \
-o Global.dataset_dir=./dataset/Inshop_examples \
-o CheckDataset.split.enable=True \
-o CheckDataset.split.train_percent=70 \
-o CheckDataset.split.gallery_percent=20 \
-o CheckDataset.split.query_percent=10
❗Note: Due to the specificity of image feature model evaluation, data partitioning is meaningful only when the train, query, and gallery sets belong to the same category system. During the evaluation of recognition models, it is imperative that the gallery and query sets belong to the same category system, which may or may not be the same as the train set. If the gallery and query sets do not belong to the same category system as the train set, the evaluation after data partitioning becomes meaningless. It is recommended to proceed with caution.
👉 More Details (Click to Expand)
- During model training, PaddleX automatically saves the model weight files, with the default being
output. If you need to specify a save path, you can set it through the -o Global.output field in the configuration file.
- PaddleX shields you from the concepts of dynamic graph weights and static graph weights. During model training, both dynamic and static graph weights are produced, and static graph weights are selected by default for model inference.
-
After completing the model training, all outputs are saved in the specified output directory (default is ./output/), typically including:
-
train_result.json: Training result record file, recording whether the training task was completed normally, as well as the output weight metrics, related file paths, etc.;
train.log: Training log file, recording changes in model metrics and loss during training;config.yaml: Training configuration file, recording the hyperparameter configuration for this training session;.pdparams, .pdema, .pdopt.pdstate, .pdiparams, .json: Model weight-related files, including network parameters, optimizer, EMA, static graph network parameters, static graph network structure, etc.;- Notice: Since Paddle 3.0.0, the format of storing static graph network structure has changed to json(the current
.json file) from protobuf(the former.pdmodel file) to be compatible with PIR and more flexible and scalable.
👉 More Details (Click to Expand)
When evaluating the model, you need to specify the model weights file path. Each configuration file has a default weight save path built-in. If you need to change it, simply set it by appending a command line parameter, such as -o Evaluate.weight_path=./output/best_model/best_model.pdparams.
After completing the model evaluation, an evaluate_result.json file will be produced, which records the evaluation results, specifically, whether the evaluation task was completed successfully and the model's evaluation metrics, including recall1、recall5、mAP;
