| Method |
Description |
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
Default |
print() |
Print results to the terminal |
format_json |
bool |
Whether to format the output content using JSON indentation |
True |
indent |
int |
Specify the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable. Only effective when format_json is True |
4 |
ensure_ascii |
bool |
Control whether to escape non-ASCII characters to Unicode. When set to True, all non-ASCII characters will be escaped; False will retain the original characters. Only effective when format_json is True |
False |
save_to_json() |
Save results as a JSON file |
save_path |
str |
Path to save the file. If it is a directory, the saved file will be named the same as the input file type |
None |
indent |
int |
Specify the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable. Only effective when format_json is True |
4 |
ensure_ascii |
bool |
Control whether to escape non-ASCII characters to Unicode. When set to True, all non-ASCII characters will be escaped; False will retain the original characters. Only effective when format_json is True |
False |
save_to_img() |
Save results as an image file |
save_path |
str |
Path to save the file. Supports directory or file path |
None |
- Calling the `print()` method will print the results to the terminal. The content printed to the terminal is explained as follows:
- `input_path`: `(str)` The input path of the image to be predicted
- `pred`: `(str)` The prediction result. Due to the large number of pixel values, `...` is used here instead of printing.
- Calling the `save_to_json()` method will save the above content to the specified `save_path`. If specified as a directory, the saved path will be `save_path/{your_img_basename}_res.json`. If specified as a file, it will be saved directly to that file. Since JSON files do not support saving numpy arrays, `numpy.array` types will be converted to lists.
- Calling the `save_to_img()` method will save the visualization results to the specified `save_path`. If specified as a directory, the saved path will be `save_path/{your_img_basename}_res.{your_img_extension}`. If specified as a file, it will be saved directly to that file. (Since the pipeline usually contains many result images, it is not recommended to specify a specific file path directly, otherwise multiple images will be overwritten, leaving only the last image)
* Additionally, it also supports obtaining visualized images and prediction results through attributes, as follows:
API Reference
For the main operations provided by the service:
- The HTTP request method is POST.
- Both the request body and response body are JSON data (JSON objects).
- When the request is successfully processed, the response status code is
200, and the attributes of the response body are as follows:
| Name |
Type |
Meaning |
logId |
string |
The UUID of the request. |
errorCode |
integer |
Error code. Fixed to 0. |
errorMsg |
string |
Error description. Fixed to "Success". |
result |
object |
Operation result. |
- When the request is not successfully processed, the attributes of the response body are as follows:
| Name |
Type |
Meaning |
logId |
string |
The UUID of the request. |
errorCode |
integer |
Error code. Same as the response status code. |
errorMsg |
string |
Error description. |
The main operations provided by the service are as follows:
Perform anomaly detection on the image.
POST /anomaly-detection
- The attributes of the request body are as follows:
| Name |
Type |
Meaning |
Required |
image |
string |
The URL of the image file accessible by the server or the Base64 encoded result of the image file content. |
Yes |
- When the request is successfully processed, the
result of the response body has the following attributes:
| Name |
Type |
Meaning |
labelMap |
array |
Records the category label of each pixel in the image (arranged in row-first order). Where 255 indicates an anomaly point, and 0 indicates a non-anomaly point. |
size |
array |
Image shape. The elements in the array are the height and width of the image in order. |
image |
string |
Anomaly detection result image. The image is in JPEG format and encoded using Base64. |
An example of result is as follows:
{
"labelMap": [
0,
0,
255,
0
],
"size": [
2,
2
],
"image": "xxxxxx"
}
Multi-language Service Invocation Example
Python
import base64
import requests
API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/image-anomaly-detection" # Service URL
image_path = "./demo.jpg"
output_image_path = "./out.jpg"
# Encode the local image using Base64
with open(image_path, "rb") as file:
image_bytes = file.read()
image_data = base64.b64encode(image_bytes).decode("ascii")
payload = {"image": image_data} # Base64-encoded file content or image URL
# Call the API
response = requests.post(API_URL, json=payload)
# Process the response data
assert response.status_code == 200
result = response.json()["result"]
with open(output_image_path, "wb") as file:
file.write(base64.b64decode(result["image"]))
print(f"Output image saved at {output_image_path}")
# result.labelMap records the class labels for each pixel in the image (arranged in row-major order). See the API reference for details.
C++
#include
#include "cpp-httplib/httplib.h" // https://github.com/Huiyicc/cpp-httplib
#include "nlohmann/json.hpp" // https://github.com/nlohmann/json
#include "base64.hpp" // https://github.com/tobiaslocker/base64
int main() {
httplib::Client client("localhost:8080");
const std::string imagePath = "./demo.jpg";
const std::string outputImagePath = "./out.jpg";
httplib::Headers headers = {
{"Content-Type", "application/json"}
};
// Encode the local image using Base64
std::ifstream file(imagePath, std::ios::binary | std::ios::ate);
std::streamsize size = file.tellg();
file.seekg(0, std::ios::beg);
std::vector buffer(size);
if (!file.read(buffer.data(), size)) {
std::cerr << "Error reading file." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
std::string bufferStr(reinterpret_cast(buffer.data()), buffer.size());
std::string encodedImage = base64::to_base64(bufferStr);
nlohmann::json jsonObj;
jsonObj["image"] = encodedImage;
std::string body = jsonObj.dump();
// Call the API
auto response = client.Post("/image-anomaly-detection", headers, body, "application/json");
// Process the response data
if (response && response->status == 200) {
nlohmann::json jsonResponse = nlohmann::json::parse(response->body);
auto result = jsonResponse["result"];
encodedImage = result["image"];
std::string decodedString = base64::from_base64(encodedImage);
std::vector decodedImage(decodedString.begin(), decodedString.end());
std::ofstream outputImage(outputImagePath, std::ios::binary | std::ios::out);
if (outputImage.is_open()) {
outputImage.write(reinterpret_cast(decodedImage.data()), decodedImage.size());
outputImage.close();
std::cout << "Output image saved at " << outputImagePath << std::endl;
// result.labelMap records the class labels for each pixel in the image (arranged in row-major order). See the API reference for details.
} else {
std::cerr << "Unable to open file for writing: " << outputImagePath << std::endl;
}
} else {
std::cout << "Failed to send HTTP request." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
Java
import okhttp3.*;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.ObjectNode;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Base64;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/image-anomaly-detection"; // Service URL
String imagePath = "./demo.jpg"; // Local image
String outputImagePath = "./out.jpg"; // Output image
// Encode the local image using Base64
File file = new File(imagePath);
byte[] fileContent = java.nio.file.Files.readAllBytes(file.toPath());
String imageData = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(fileContent);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
ObjectNode params = objectMapper.createObjectNode();
params.put("image", imageData); // Base64-encoded file content or image URL
// Create an OkHttpClient instance
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
MediaType JSON = MediaType.Companion.get("application/json; charset=utf-8");
RequestBody body = RequestBody.Companion.create(params.toString(), JSON);
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(API_URL)
.post(body)
.build();
// Call the API and process the response data
try (Response response = client.newCall(request).execute()) {
if (response.isSuccessful()) {
String responseBody = response.body().string();
JsonNode resultNode = objectMapper.readTree(responseBody);
JsonNode result = resultNode.get("result");
String base64Image = result.get("image").asText();
JsonNode labelMap = result.get("labelMap");
byte[] imageBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(base64Image);
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(outputImagePath)) {
fos.write(imageBytes);
}
System.out.println("Output image saved at " + outputImagePath);
// result.labelMap contains the class labels for each pixel in the image (arranged in row-major order). See the API reference documentation for details.
} else {
System.err.println("Request failed with code: " + response.code());
}
}
}
}
Go
package main
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
API_URL := "http://localhost:8080/image-anomaly-detection"
imagePath := "./demo.jpg"
outputImagePath := "./out.jpg"
// Base64 encode the local image
imageBytes, err := ioutil.ReadFile(imagePath)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error reading image file:", err)
return
}
imageData := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(imageBytes)
payload := map[string]string{"image": imageData} // Base64 encoded file content or image URL
payloadBytes, err := json.Marshal(payload)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error marshaling payload:", err)
return
}
// Call the API
client := &http.Client{}
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", API_URL, bytes.NewBuffer(payloadBytes))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error creating request:", err)
return
}
res, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error sending request:", err)
return
}
defer res.Body.Close()
// Process the returned data from the API
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error reading response body:", err)
return
}
type Response struct {
Result struct {
Image string `json:"image"`
Labelmap []map[string]interface{} `json:"labelMap"`
} `json:"result"`
}
var respData Response
err = json.Unmarshal([]byte(string(body)), &respData)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error unmarshaling response body:", err)
return
}
outputImageData, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(respData.Result.Image)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error decoding base64 image data:", err)
return
}
err = ioutil.WriteFile(outputImagePath, outputImageData, 0644)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error writing image to file:", err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("Image saved at %s.jpg\n", outputImagePath)
// result.labelMap records the category label of each pixel in the image (arranged in row-first order). See the API reference documentation for details.
}
C#
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Net.Http.Headers;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Newtonsoft.Json.Linq;
class Program
{
static readonly string API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/image-anomaly-detection";
static readonly string imagePath = "./demo.jpg";
static readonly string outputImagePath = "./out.jpg";
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
var httpClient = new HttpClient();
// Base64 encode the local image
byte[] imageBytes = File.ReadAllBytes(imagePath);
string image_data = Convert.ToBase64String(imageBytes);
var payload = new JObject{ { "image", image_data } }; // Base64 encoded file content or image URL
var content = new StringContent(payload.ToString(), Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
// Call the API
HttpResponseMessage response = await httpClient.PostAsync(API_URL, content);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
// Process the API response
string responseBody = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
JObject jsonResponse = JObject.Parse(responseBody);
string base64Image = jsonResponse["result"]["image"].ToString();
byte[] outputImageBytes = Convert.FromBase64String(base64Image);
File.WriteAllBytes(outputImagePath, outputImageBytes);
Console.WriteLine($"Output image saved at {outputImagePath}");
// result.labelMap records the category label of each pixel in the image (arranged in row-first order). See API reference documentation for details.
}
}
Node.js
const axios = require('axios');
const fs = require('fs');
const API_URL = 'http://localhost:8080/image-anomaly-detection';
const imagePath = './demo.jpg';
const outputImagePath = './out.jpg';
let config = {
method: 'POST',
maxBodyLength: Infinity,
url: API_URL,
data: JSON.stringify({
'image': encodeImageToBase64(imagePath) // Base64-encoded file content or image URL
})
};
// Encode the local image using Base64
function encodeImageToBase64(filePath) {
const bitmap = fs.readFileSync(filePath);
return Buffer.from(bitmap).toString('base64');
}
// Call the API
axios.request(config)
.then((response) => {
// Process the response data
const result = response.data['result'];
const imageBuffer = Buffer.from(result['image'], 'base64');
fs.writeFile(outputImagePath, imageBuffer, (err) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(`Output image saved at ${outputImagePath}`);
});
// result.labelMap records the class labels for each pixel in the image (arranged in row-major order). See the API reference for details.
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log(error);
});
PHP
<?php
$API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/image-anomaly-detection"; // Service URL
$image_path = "./demo.jpg";
$output_image_path = "./out.jpg";
// Encode the local image using Base64
$image_data = base64_encode(file_get_contents($image_path));
$payload = array("image" => $image_data); // Base64-encoded file content or image URL
// Call the API
$ch = curl_init($API_URL);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, json_encode($payload));
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, array('Content-Type: application/json'));
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
$response = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
// Process the response data
$result = json_decode($response, true)["result"];
file_put_contents($output_image_path, base64_decode($result["image"]));
echo "Output image saved at " . $output_image_path . "\n";
// result.labelMap contains the class labels for each pixel in the image (arranged in row-major order). See the API reference documentation for details.
?>
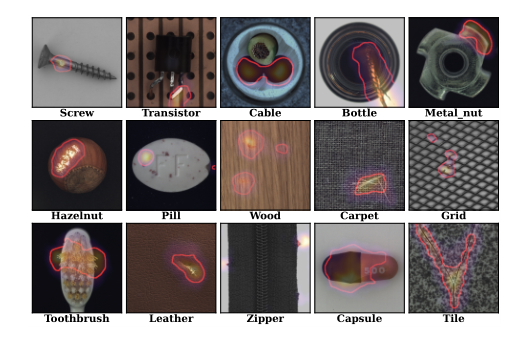 The image anomaly detection pipeline includes an unsupervised anomaly detection module, with the following model benchmarks:
The image anomaly detection pipeline includes an unsupervised anomaly detection module, with the following model benchmarks:
 ### 2.2 Python Script Integration
The above command line is for quickly experiencing and checking the effect. Generally, in a project, it is often necessary to integrate through code. You can complete the quick inference of the production line with a few lines of code. The inference code is as follows:
```python
from paddlex import create_pipeline
pipeline = create_pipeline(pipeline="anomaly_detection")
output = pipeline.predict(input="uad_grid.png")
for res in output:
res.print() ## 打印预测的结构化输出
res.save_to_img(save_path="./output/") ## 保存结果可视化图像
res.save_to_json(save_path="./output/") ## 保存预测的结构化输出
```
In the above Python script, the following steps are executed:
(1) Instantiate the pipeline object through `create_pipeline()`: The specific parameter descriptions are as follows:
### 2.2 Python Script Integration
The above command line is for quickly experiencing and checking the effect. Generally, in a project, it is often necessary to integrate through code. You can complete the quick inference of the production line with a few lines of code. The inference code is as follows:
```python
from paddlex import create_pipeline
pipeline = create_pipeline(pipeline="anomaly_detection")
output = pipeline.predict(input="uad_grid.png")
for res in output:
res.print() ## 打印预测的结构化输出
res.save_to_img(save_path="./output/") ## 保存结果可视化图像
res.save_to_json(save_path="./output/") ## 保存预测的结构化输出
```
In the above Python script, the following steps are executed:
(1) Instantiate the pipeline object through `create_pipeline()`: The specific parameter descriptions are as follows: