---
comments: true
---
# PaddleX Image Classification Task Module Data Annotation Tutorial
This document will introduce how to use the [Labelme](https://github.com/wkentaro/labelme) annotation tool to complete data annotation for image classification related single models.
Click on the above link to refer to the homepage documentation for installing the data annotation tool and viewing detailed usage procedures.
## 1. Labelme Annotation
### 1.1 Introduction to Labelme Annotation Tool
`Labelme` is a Python-based image annotation software with a graphical interface. It can be used for tasks such as image classification, object detection, and image segmentation. In instance segmentation annotation tasks, labels are stored as `JSON` files.
### 1.2 Labelme Installation
To avoid environment conflicts, it is recommended to install in a `conda` environment.
```bash
conda create -n labelme python=3.10
conda activate labelme
pip install pyqt5
pip install labelme
```
### 1.3 Labelme Annotation Process
#### 1.3.1 Prepare Data for Annotation
* Create a root directory for the dataset, such as `pets`.
* Create an `images` directory (must be named `images`) within `pets` and store the images to be annotated in the `images` directory, as shown below:
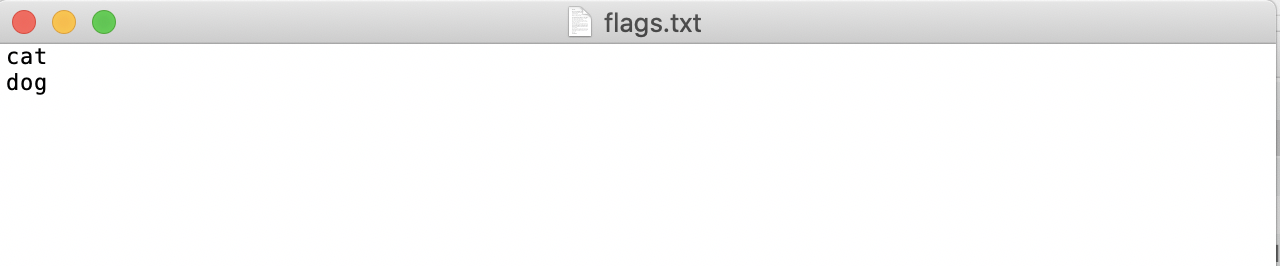
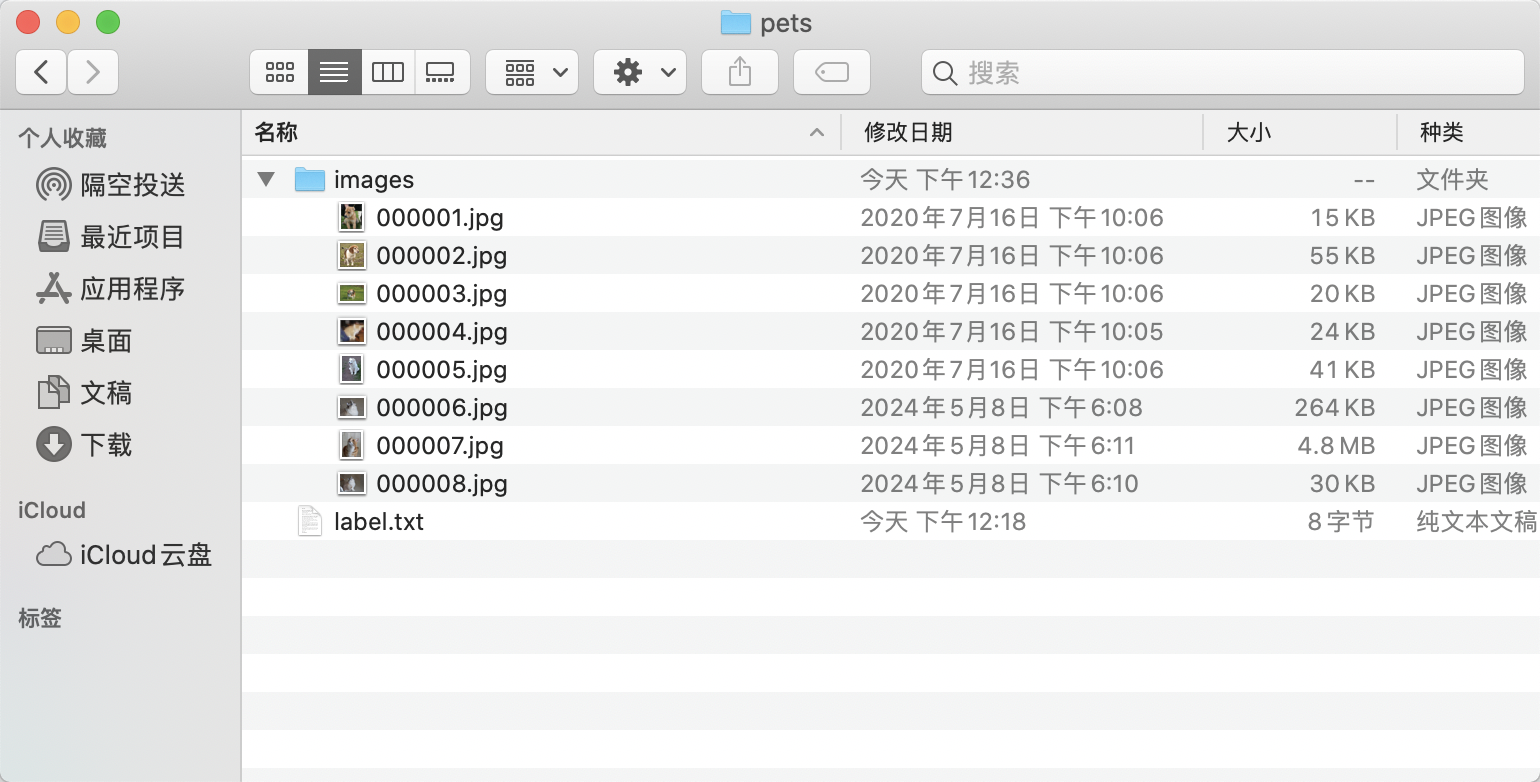 * Create a category label file `flags.txt` for the dataset to be annotated in the `pets` folder, and write the categories of the dataset to be annotated into `flags.txt` line by line. Taking the `flags.txt` for a cat and dog classification dataset as an example, as shown below:
* Create a category label file `flags.txt` for the dataset to be annotated in the `pets` folder, and write the categories of the dataset to be annotated into `flags.txt` line by line. Taking the `flags.txt` for a cat and dog classification dataset as an example, as shown below:
 #### 1.3.2 Start Labelme
Navigate to the root directory of the dataset to be annotated in the terminal and start the `labelme` annotation tool.
```bash
cd path/to/pets
labelme images --nodata --autosave --output annotations --flags flags.txt
```
* `flags` creates classification labels for images, passing in the path to the labels.
* `nodata` stops storing image data in JSON files.
* `autosave` enables automatic saving.
* `output` specifies the storage path for label files.
#### 1.3.3 Start Image Annotation
* After starting `labelme`, it will look like this:
#### 1.3.2 Start Labelme
Navigate to the root directory of the dataset to be annotated in the terminal and start the `labelme` annotation tool.
```bash
cd path/to/pets
labelme images --nodata --autosave --output annotations --flags flags.txt
```
* `flags` creates classification labels for images, passing in the path to the labels.
* `nodata` stops storing image data in JSON files.
* `autosave` enables automatic saving.
* `output` specifies the storage path for label files.
#### 1.3.3 Start Image Annotation
* After starting `labelme`, it will look like this:
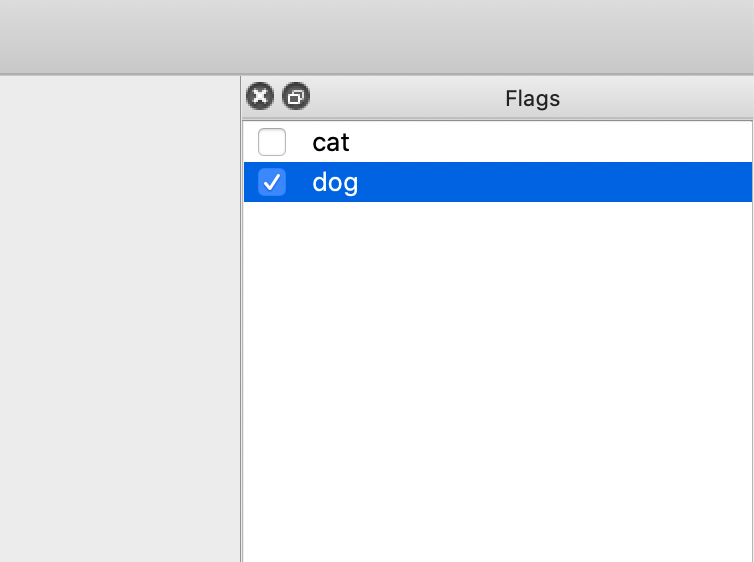
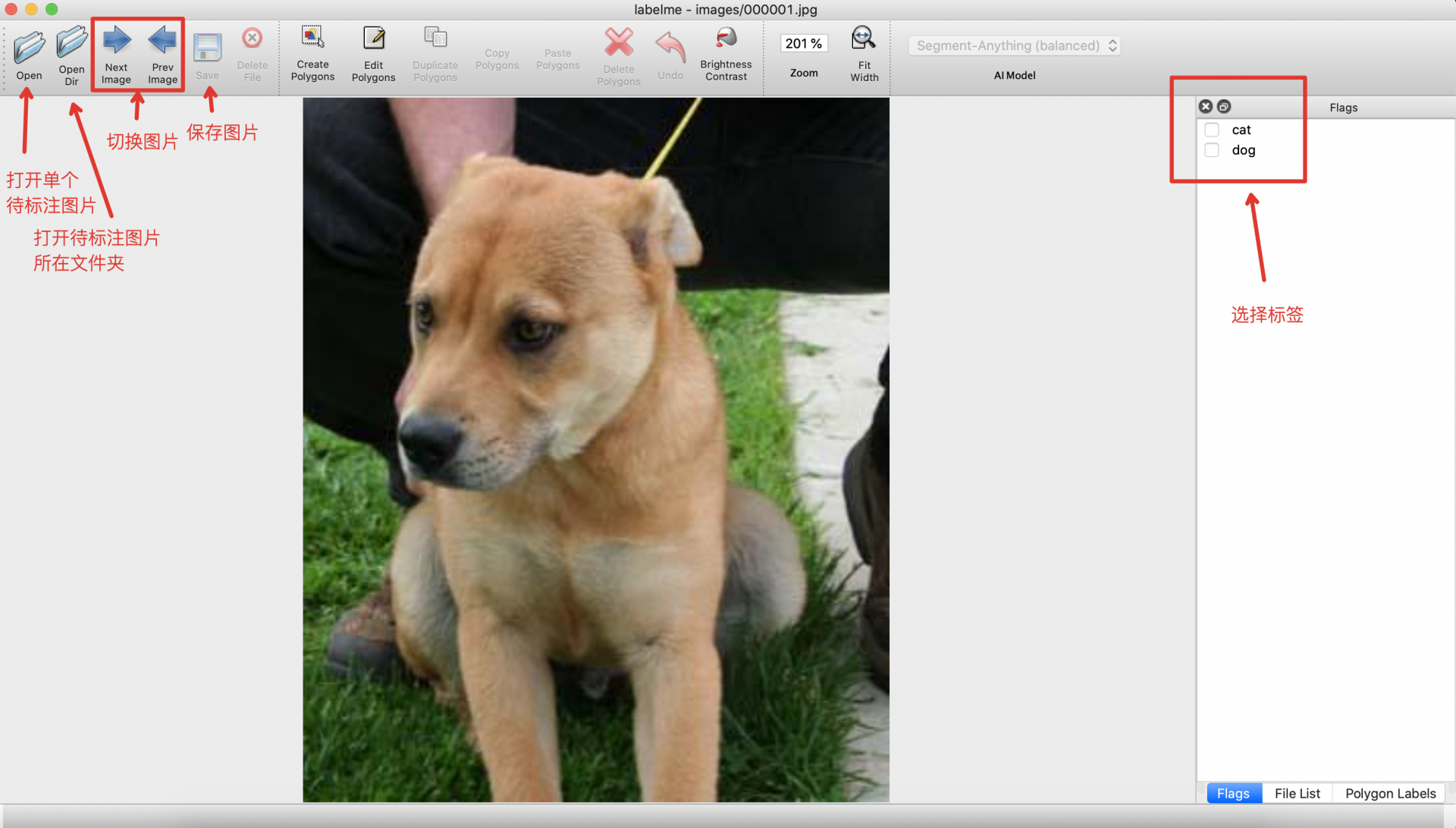 * Select the category in the `Flags` interface.
* Select the category in the `Flags` interface.
 * After annotation, click Save. (If `output` is not specified when starting `labelme`, it will prompt to select a save path upon the first save. If `autosave` is specified, there is no need to click the Save button).
* After annotation, click Save. (If `output` is not specified when starting `labelme`, it will prompt to select a save path upon the first save. If `autosave` is specified, there is no need to click the Save button).
 * Then click `Next Image` to annotate the next image.
* Then click `Next Image` to annotate the next image.
 * After annotating all images, use the [convert_to_imagenet.py](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/PaddleX3.0/doc_images/applications/image_classification_dataset_prepare/convert_to_imagenet.py) script to convert the annotated dataset to the `ImageNet-1k` dataset format, generating `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `label.txt`.
```bash
python convert_to_imagenet.py --dataset_path /path/to/dataset
```
`dataset_path` is the path to the annotated `labelme` format classification dataset.
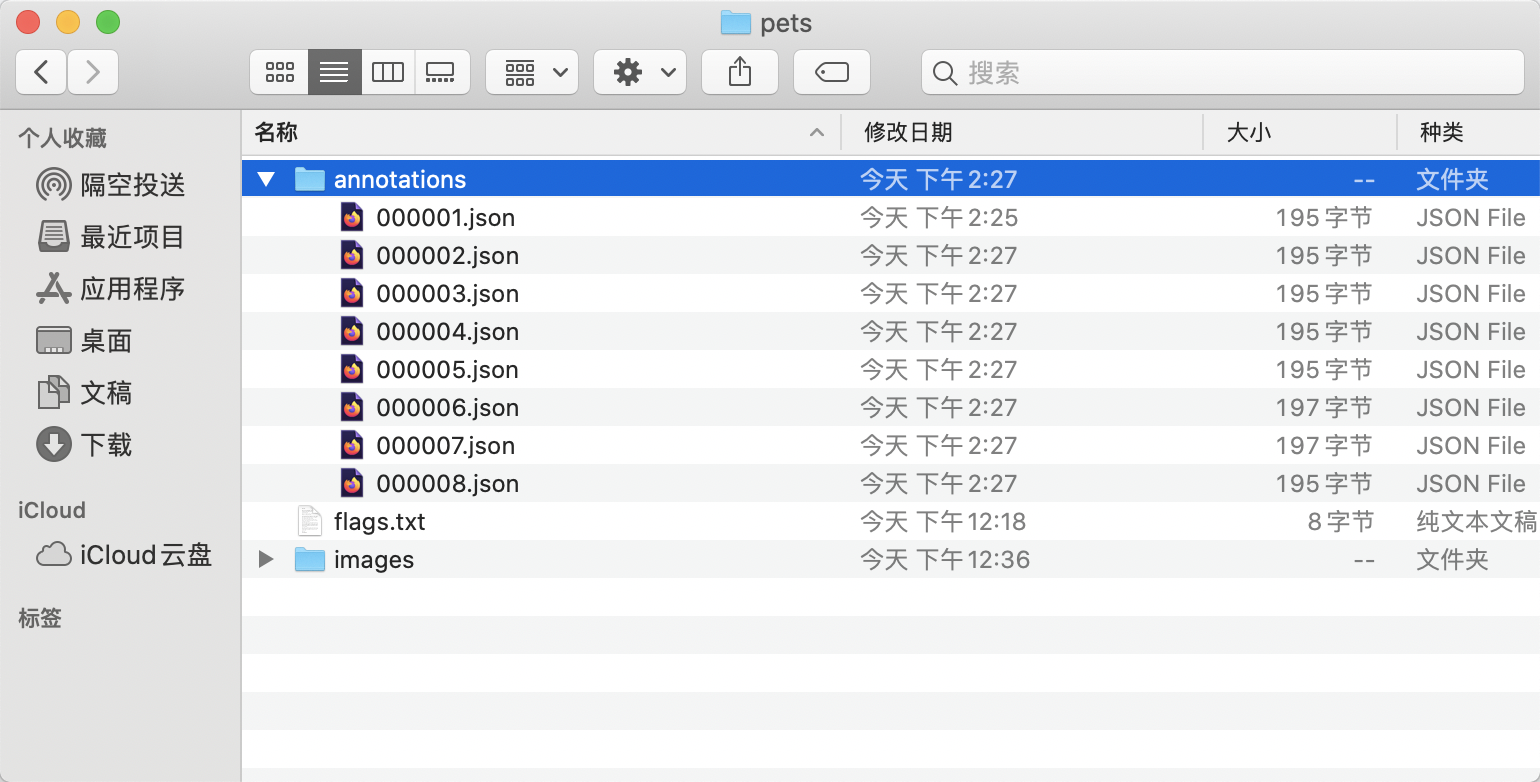
* The final directory structure after organization is as follows:
* After annotating all images, use the [convert_to_imagenet.py](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/PaddleX3.0/doc_images/applications/image_classification_dataset_prepare/convert_to_imagenet.py) script to convert the annotated dataset to the `ImageNet-1k` dataset format, generating `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `label.txt`.
```bash
python convert_to_imagenet.py --dataset_path /path/to/dataset
```
`dataset_path` is the path to the annotated `labelme` format classification dataset.
* The final directory structure after organization is as follows:
 ## 2. Data Format
* The dataset defined by PaddleX for image classification tasks is named ClsDataset, with the following organizational structure and annotation format:
```bash
dataset_dir # Root directory of the dataset, the directory name can be changed
├── images # Directory for saving images, the directory name can be changed, but note the correspondence with the content of train.txt and val.txt
├── label.txt # Correspondence between annotation IDs and category names, the file name cannot```bash
classname1
classname2
classname3
...
```
Modified `label.txt`:
```bash
0 classname1
1 classname2
2 classname3
...
## 2. Data Format
* The dataset defined by PaddleX for image classification tasks is named ClsDataset, with the following organizational structure and annotation format:
```bash
dataset_dir # Root directory of the dataset, the directory name can be changed
├── images # Directory for saving images, the directory name can be changed, but note the correspondence with the content of train.txt and val.txt
├── label.txt # Correspondence between annotation IDs and category names, the file name cannot```bash
classname1
classname2
classname3
...
```
Modified `label.txt`:
```bash
0 classname1
1 classname2
2 classname3
...
 * Create a category label file `flags.txt` for the dataset to be annotated in the `pets` folder, and write the categories of the dataset to be annotated into `flags.txt` line by line. Taking the `flags.txt` for a cat and dog classification dataset as an example, as shown below:
* Create a category label file `flags.txt` for the dataset to be annotated in the `pets` folder, and write the categories of the dataset to be annotated into `flags.txt` line by line. Taking the `flags.txt` for a cat and dog classification dataset as an example, as shown below:
 #### 1.3.2 Start Labelme
Navigate to the root directory of the dataset to be annotated in the terminal and start the `labelme` annotation tool.
```bash
cd path/to/pets
labelme images --nodata --autosave --output annotations --flags flags.txt
```
* `flags` creates classification labels for images, passing in the path to the labels.
* `nodata` stops storing image data in JSON files.
* `autosave` enables automatic saving.
* `output` specifies the storage path for label files.
#### 1.3.3 Start Image Annotation
* After starting `labelme`, it will look like this:
#### 1.3.2 Start Labelme
Navigate to the root directory of the dataset to be annotated in the terminal and start the `labelme` annotation tool.
```bash
cd path/to/pets
labelme images --nodata --autosave --output annotations --flags flags.txt
```
* `flags` creates classification labels for images, passing in the path to the labels.
* `nodata` stops storing image data in JSON files.
* `autosave` enables automatic saving.
* `output` specifies the storage path for label files.
#### 1.3.3 Start Image Annotation
* After starting `labelme`, it will look like this:
 * Select the category in the `Flags` interface.
* Select the category in the `Flags` interface.
 * After annotation, click Save. (If `output` is not specified when starting `labelme`, it will prompt to select a save path upon the first save. If `autosave` is specified, there is no need to click the Save button).
* After annotation, click Save. (If `output` is not specified when starting `labelme`, it will prompt to select a save path upon the first save. If `autosave` is specified, there is no need to click the Save button).
 * Then click `Next Image` to annotate the next image.
* Then click `Next Image` to annotate the next image.
 * After annotating all images, use the [convert_to_imagenet.py](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/PaddleX3.0/doc_images/applications/image_classification_dataset_prepare/convert_to_imagenet.py) script to convert the annotated dataset to the `ImageNet-1k` dataset format, generating `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `label.txt`.
```bash
python convert_to_imagenet.py --dataset_path /path/to/dataset
```
`dataset_path` is the path to the annotated `labelme` format classification dataset.
* The final directory structure after organization is as follows:
* After annotating all images, use the [convert_to_imagenet.py](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/PaddleX3.0/doc_images/applications/image_classification_dataset_prepare/convert_to_imagenet.py) script to convert the annotated dataset to the `ImageNet-1k` dataset format, generating `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `label.txt`.
```bash
python convert_to_imagenet.py --dataset_path /path/to/dataset
```
`dataset_path` is the path to the annotated `labelme` format classification dataset.
* The final directory structure after organization is as follows:
 ## 2. Data Format
* The dataset defined by PaddleX for image classification tasks is named ClsDataset, with the following organizational structure and annotation format:
```bash
dataset_dir # Root directory of the dataset, the directory name can be changed
├── images # Directory for saving images, the directory name can be changed, but note the correspondence with the content of train.txt and val.txt
├── label.txt # Correspondence between annotation IDs and category names, the file name cannot```bash
classname1
classname2
classname3
...
```
Modified `label.txt`:
```bash
0 classname1
1 classname2
2 classname3
...
## 2. Data Format
* The dataset defined by PaddleX for image classification tasks is named ClsDataset, with the following organizational structure and annotation format:
```bash
dataset_dir # Root directory of the dataset, the directory name can be changed
├── images # Directory for saving images, the directory name can be changed, but note the correspondence with the content of train.txt and val.txt
├── label.txt # Correspondence between annotation IDs and category names, the file name cannot```bash
classname1
classname2
classname3
...
```
Modified `label.txt`:
```bash
0 classname1
1 classname2
2 classname3
...