| Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Options |
Default |
input |
Data to be predicted, supports multiple input types, required |
Python Var|str|list |
- Python Var: Image data represented by
numpy.ndarray
- str: Local path of an image file or PDF file, such as
/root/data/img.jpg; URL link, such as a network URL of an image file or PDF file: Example; Local directory, which should contain images to be predicted, such as /root/data/ (currently does not support prediction of directories containing PDF files, PDF files need to be specified to specific file paths)
- List: Elements of the list must be of the above types, such as
[numpy.ndarray, numpy.ndarray], ["/root/data/img1.jpg", "/root/data/img2.jpg"], ["/root/data1", "/root/data2"]
|
None |
threshold |
Low score object filtering threshold for the model |
float|None |
- float: Any floating-point number greater than
0 and less than 1
- None: If set to
None, the default parameter 0.5 of the pipeline will be used as the threshold
|
None |
(3) Process the prediction results. The prediction result for each sample is of type `dict` and supports operations such as printing, saving as an image, and saving as a `json` file:
| Method |
Description |
Parameter |
Type |
Parameter Description |
Default Value |
print() |
Print the result to the terminal |
format_json |
bool |
Whether to format the output content using JSON indentation |
True |
indent |
int |
Specify the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable. Effective only when format_json is True |
4 |
ensure_ascii |
bool |
Control whether non-ASCII characters are escaped to Unicode. When set to True, all non-ASCII characters will be escaped; False retains the original characters. Effective only when format_json is True |
False |
save_to_json() |
Save the result as a json file |
save_path |
str |
Path to save the file. If it is a directory, the saved file name will be consistent with the input file type |
None |
indent |
int |
Specify the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable. Effective only when format_json is True |
4 |
ensure_ascii |
bool |
Control whether non-ASCII characters are escaped to Unicode. When set to True, all non-ASCII characters will be escaped; False retains the original characters. Effective only when format_json is True |
False |
save_to_img() |
Save the result as an image file |
save_path |
str |
Path to save the file. Supports directory or file path |
None |
- Calling the `print()` method will print the result to the terminal. The content printed to the terminal is explained as follows:
- `input_path`: `(str)` Input path of the image to be predicted
- `page_index`: `(Union[int, None])` If the input is a PDF file, it indicates the current page of the PDF; otherwise, it is `None`
- `boxes`: `(list)` Detection box information, each element is a dictionary containing the following fields:
- `cls_id`: `(int)` Class ID
- `label`: `(str)` Class name
- `score`: `(float)` Confidence of the detection box
- `coordinate`: `(list)` Coordinates of the detection box, in the format [xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax]
- `masks`: `...` The actual predicted mask of the instance segmentation model. Due to the large amount of data, it is not convenient to print directly, so it is replaced with `...`. You can save the prediction result as an image using `res.save_to_img` or save it as a json file using `res.save_to_json`.
- Calling the `save_to_json()` method will save the above content to the specified `save_path`. If specified as a directory, the saved path will be `save_path/{your_img_basename}_res.json`. If specified as a file, it will be saved directly to that file. Since json files do not support saving numpy arrays, `numpy.array` types will be converted to lists.
- Calling the `save_to_img()` method will save the visualization result to the specified `save_path`. If specified as a directory, the saved path will be `save_path/{your_img_basename}_res.{your_img_extension}`. If specified as a file, it will be saved directly to that file.
* In addition, you can also obtain the visualized image and prediction results through attributes, as follows:
API Reference
For the main operations provided by the service:
- The HTTP request method is POST.
- Both the request body and response body are JSON data (JSON objects).
- When the request is successfully processed, the response status code is
200, and the attributes of the response body are as follows:
| Name |
Type |
Meaning |
logId |
string |
The UUID of the request. |
errorCode |
integer |
Error code. Fixed at 0. |
errorMsg |
string |
Error description. Fixed at "Success". |
result |
object |
Operation result. |
- When the request is not successfully processed, the attributes of the response body are as follows:
| Name |
Type |
Meaning |
logId |
string |
The UUID of the request. |
errorCode |
integer |
Error code. Same as the response status code. |
errorMsg |
string |
Error description. |
The main operations provided by the service are as follows:
Perform instance segmentation on an image.
POST /instance-segmentation
- The attributes of the request body are as follows:
| Name |
Type |
Meaning |
Required |
image |
string |
The URL of the image file accessible by the server or the Base64 encoded content of the image file. |
Yes |
threshold |
number | null |
Please refer to the description of the threshold parameter of the pipeline object's predict method. |
No |
visualize |
boolean | null |
Whether to return the final visualization image and intermediate images during the processing.
- If
true is provided: return images.
- If
false is provided: do not return any images.
- If this parameter is omitted from the request body, or if
null is explicitly passed, the behavior will follow the value of Serving.visualize in the pipeline configuration.
For example, adding the following setting to the pipeline config file:
Serving:
visualize: False
will disable image return by default. This behavior can be overridden by explicitly setting the visualize parameter in the request.
If neither the request body nor the configuration file is set (If visualize is set to null in the request and not defined in the configuration file), the image is returned by default.
|
No |
- When the request is successfully processed, the
result of the response body has the following attributes:
| Name |
Type |
Meaning |
instances |
array |
Information about the location, category, and other details of instances. |
image |
string| null |
The result image of instance segmentation. The image is in JPEG format and encoded using Base64. |
Each element in instances is an object with the following attributes:
| Name |
Type |
Meaning |
bbox |
array |
The location of the instance. The elements in the array are the x-coordinate of the top-left corner, the y-coordinate of the top-left corner, the x-coordinate of the bottom-right corner, and the y-coordinate of the bottom-right corner. |
categoryId |
integer |
The category ID of the instance. |
categoryName |
string |
The label name of the instance category. |
score |
number |
The score of the instance. |
mask |
object |
The segmentation mask of the instance. |
The attributes of mask are as follows:
| Name |
Type |
Meaning |
rleResult |
str |
The run-length encoding result of the mask. |
size |
array |
The shape of the mask. The elements in the array are the height and width of the mask. |
result example is as follows:
{
"instances": [
{
"bbox": [
162.39381408691406,
83.88176727294922,
624.0797119140625,
343.4986877441406
],
"categoryId": 33,
"score": 0.8691174983978271,
"mask": {
"rleResult": "xxxxxx",
"size": [
259,
462
]
}
}
],
"image": "xxxxxx"
}
Multi-Language Service Call Examples
Python
import base64
import requests
API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/instance-segmentation" # Service URL
image_path = "./demo.jpg"
output_image_path = "./out.jpg"
# Encode the local image using Base64
with open(image_path, "rb") as file:
image_bytes = file.read()
image_data = base64.b64encode(image_bytes).decode("ascii")
payload = {"image": image_data} # Base64-encoded file content or image URL
# Call the API
response = requests.post(API_URL, json=payload)
# Process the response data
assert response.status_code == 200
result = response.json()["result"]
with open(output_image_path, "wb") as file:
file.write(base64.b64decode(result["image"]))
print(f"Output image saved at {output_image_path}")
print("\nInstances:")
print(result["instances"])
C++
#include <iostream>
#include "cpp-httplib/httplib.h" // https://github.com/Huiyicc/cpp-httplib
#include "nlohmann/json.hpp" // https://github.com/nlohmann/json
#include "base64.hpp" // https://github.com/tobiaslocker/base64
int main() {
httplib::Client client("localhost:8080");
const std::string imagePath = "./demo.jpg";
const std::string outputImagePath = "./out.jpg";
httplib::Headers headers = {
{"Content-Type", "application/json"}
};
// Encode the local image using Base64
std::ifstream file(imagePath, std::ios::binary | std::ios::ate);
std::streamsize size = file.tellg();
file.seekg(0, std::ios::beg);
std::vector<char> buffer(size);
if (!file.read(buffer.data(), size)) {
std::cerr << "Error reading file." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
std::string bufferStr(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(buffer.data()), buffer.size());
std::string encodedImage = base64::to_base64(bufferStr);
nlohmann::json jsonObj;
jsonObj["image"] = encodedImage;
std::string body = jsonObj.dump();
// Call the API
auto response = client.Post("/instance-segmentation", headers, body, "application/json");
// Process the response data
if (response && response->status == 200) {
nlohmann::json jsonResponse = nlohmann::json::parse(response->body);
auto result = jsonResponse["result"];
encodedImage = result["image"];
std::string decodedString = base64::from_base64(encodedImage);
std::vector<unsigned char> decodedImage(decodedString.begin(), decodedString.end());
std::ofstream outputImage(outputImagePath, std::ios::binary | std::ios::out);
if (outputImage.is_open()) {
outputImage.write(reinterpret_cast<char*>(decodedImage.data()), decodedImage.size());
outputImage.close();
std::cout << "Output image saved at " << outputImagePath << std::endl;
} else {
std::cerr << "Unable to open file for writing: " << outputImagePath << std::endl;
}
auto instances = result["instances"];
std::cout << "\nInstances:" << std::endl;
for (const auto& inst : instances) {
std::cout << inst << std::endl;
}
} else {
std::cout << "Failed to send HTTP request." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
Java
import okhttp3.*;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.ObjectNode;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Base64;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/instance-segmentation"; // Service URL
String imagePath = "./demo.jpg"; // Local image
String outputImagePath = "./out.jpg"; // Output image
// Encode the local image to Base64
File file = new File(imagePath);
byte[] fileContent = java.nio.file.Files.readAllBytes(file.toPath());
String imageData = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(fileContent);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
ObjectNode params = objectMapper.createObjectNode();
params.put("image", imageData); // Base64-encoded file content or image URL
// Create an OkHttpClient instance
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
MediaType JSON = MediaType.Companion.get("application/json; charset=utf-8");
RequestBody body = RequestBody.Companion.create(params.toString(), JSON);
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(API_URL)
.post(body)
.build();
// Call the API and process the response data
try (Response response = client.newCall(request).execute()) {
if (response.isSuccessful()) {
String responseBody = response.body().string();
JsonNode resultNode = objectMapper.readTree(responseBody);
JsonNode result = resultNode.get("result");
String base64Image = result.get("image").asText();
JsonNode instances = result.get("instances");
byte[] imageBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(base64Image);
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(outputImagePath)) {
fos.write(imageBytes);
}
System.out.println("Output image saved at " + outputImagePath);
System.out.println("\nInstances: " + instances.toString());
} else {
System.err.println("Request failed with code: " + response.code());
}
}
}
}
Go
package main
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
API_URL := "http://localhost:8080/instance-segmentation"
imagePath := "./demo.jpg"
outputImagePath := "./out.jpg"
// Encode the local image in Base64
imageBytes, err := ioutil.ReadFile(imagePath)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error reading image file:", err)
return
}
imageData := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(imageBytes)
payload := map[string]string{"image": imageData} // Base64 encoded file content or image URL
payloadBytes, err := json.Marshal(payload)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error marshaling payload:", err)
return
}
// Call the API
client := &http.Client{}
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", API_URL, bytes.NewBuffer(payloadBytes))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error creating request:", err)
return
}
res, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error sending request:", err)
return
}
defer res.Body.Close()
// Process the returned data
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error reading response body:", err)
return
}
type Response struct {
Result struct {
Image string `json:"image"`
Instances []map[string]interface{} `json:"instances"`
} `json:"result"`
}
var respData Response
err = json.Unmarshal([]byte(string(body)), &respData)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error unmarshaling response body:", err)
return
}
outputImageData, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(respData.Result.Image)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error decoding base64 image data:", err)
return
}
err = ioutil.WriteFile(outputImagePath, outputImageData, 0644)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error writing image to file:", err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("Image saved at %s.jpg\n", outputImagePath)
fmt.Println("\nInstances:")
for _, inst := range respData.Result.Instances {
fmt.Println(inst)
}
}
C#
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Net.Http.Headers;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Newtonsoft.Json.Linq;
class Program
{
static readonly string API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/instance-segmentation";
static readonly string imagePath = "./demo.jpg";
static readonly string outputImagePath = "./out.jpg";
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
var httpClient = new HttpClient();
// Encode the local image using Base64
byte[] imageBytes = File.ReadAllBytes(imagePath);
string image_data = Convert.ToBase64String(imageBytes);
var payload = new JObject{ { "image", image_data } }; // Base64-encoded file content or image URL
var content = new StringContent(payload.ToString(), Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
// Call the API
HttpResponseMessage response = await httpClient.PostAsync(API_URL, content);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
// Process the API response data
string responseBody = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
JObject jsonResponse = JObject.Parse(responseBody);
string base64Image = jsonResponse["result"]["image"].ToString();
byte[] outputImageBytes = Convert.FromBase64String(base64Image);
File.WriteAllBytes(outputImagePath, outputImageBytes);
Console.WriteLine($"Output image saved at {outputImagePath}");
Console.WriteLine("\nInstances:");
Console.WriteLine(jsonResponse["result"]["instances"].ToString());
}
}
Node.js
const axios = require('axios');
const fs = require('fs');
const API_URL = 'http://localhost:8080/instance-segmentation';
const imagePath = './demo.jpg';
const outputImagePath = './out.jpg';
let config = {
method: 'POST',
maxBodyLength: Infinity,
url: API_URL,
data: JSON.stringify({
'image': encodeImageToBase64(imagePath) // Base64-encoded file content or image URL
})
};
// Encode the local image using Base64
function encodeImageToBase64(filePath) {
const bitmap = fs.readFileSync(filePath);
return Buffer.from(bitmap).toString('base64');
}
// Call the API
axios.request(config)
.then((response) => {
// Process the response data
const result = response.data['result'];
const imageBuffer = Buffer.from(result['image'], 'base64');
fs.writeFile(outputImagePath, imageBuffer, (err) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(`Output image saved at ${outputImagePath}`);
});
console.log('\nInstances:');
console.log(result['instances']);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log(error);
});
PHP
<?php
$API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/instance-segmentation"; // Service URL
$image_path = "./demo.jpg";
$output_image_path = "./out.jpg";
// Encode the local image using Base64
$image_data = base64_encode(file_get_contents($image_path));
$payload = array("image" => $image_data); // Base64-encoded file content or image URL
// Call the API
$ch = curl_init($API_URL);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, json_encode($payload));
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, array('Content-Type: application/json'));
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
$response = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
// Process the response data
$result = json_decode($response, true)['result'];
file_put_contents($output_image_path, base64_decode($result['image']));
echo "Output image saved at " . $output_image_path . "\n";
echo "\nInstances:\n";
print_r($result['instances']);
?>
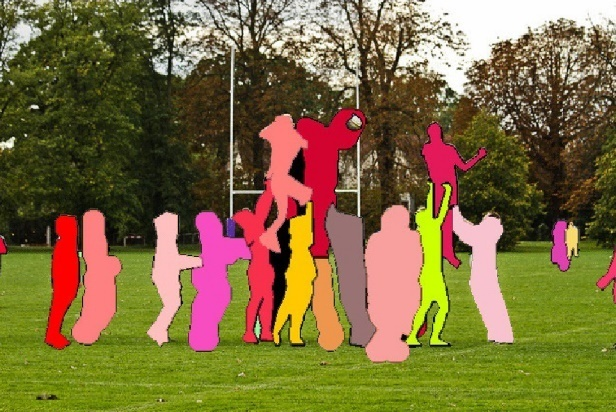 The General Instance Segmentation Pipeline includes a Object Detection module. If you prioritize model precision, choose a model with higher precision. If you prioritize inference speed, choose a model with faster inference. If you prioritize model storage size, choose a model with a smaller storage size.
The General Instance Segmentation Pipeline includes a Object Detection module. If you prioritize model precision, choose a model with higher precision. If you prioritize inference speed, choose a model with faster inference. If you prioritize model storage size, choose a model with a smaller storage size.
 If you are satisfied with the pipeline's performance, you can directly integrate and deploy it. If not, you can also use your private data to fine-tune the model within the pipeline.
### 2.2 Local Experience
> ❗ Before using the general instance segmentation pipeline locally, please ensure that you have completed the installation of the PaddleX wheel package according to the [PaddleX Local Installation Guide](../../../installation/installation.en.md). If you wish to selectively install dependencies, please refer to the relevant instructions in the installation guide. The dependency group corresponding to this pipeline is `cv`.
#### 2.2.1 Command Line Experience
* You can quickly experience the instance segmentation pipeline effect with a single command. Use the [test file](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/general_instance_segmentation_004.png), and replace `--input` with the local path for prediction.
```bash
paddlex --pipeline instance_segmentation \
--input general_instance_segmentation_004.png \
--threshold 0.5 \
--save_path ./output \
--device gpu:0
```
The relevant parameter descriptions can be referred to in the parameter explanations in [2.2.2 Python Script Integration](). Supports specifying multiple devices simultaneously for parallel inference. For details, please refer to the documentation on pipeline parallel inference.
After running, the result will be printed to the terminal as follows:
```bash
{'res': {'input_path': 'general_instance_segmentation_004.png', 'page_index': None, 'boxes': [{'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'person', 'score': 0.8695873022079468, 'coordinate': [339.83426, 0, 639.8651, 575.22003]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'person', 'score': 0.8572642803192139, 'coordinate': [0.09976959, 0, 195.07274, 575.358]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'person', 'score': 0.8201770186424255, 'coordinate': [88.24664, 113.422424, 401.23077, 574.70197]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'person', 'score': 0.7110118269920349, 'coordinate': [522.54065, 21.457964, 767.5007, 574.2464]}, {'cls_id': 27, 'label': 'tie', 'score': 0.5543721914291382, 'coordinate': [247.38776, 312.4094, 355.2685, 574.1264]}], 'masks': '...'}}
```
The explanation of the result parameters can be referred to in [2.2.2 Python Script Integration](#222-python脚本方式集成).
The visualization results are saved under `save_path`, and the visualization results of instance segmentation are as follows:
If you are satisfied with the pipeline's performance, you can directly integrate and deploy it. If not, you can also use your private data to fine-tune the model within the pipeline.
### 2.2 Local Experience
> ❗ Before using the general instance segmentation pipeline locally, please ensure that you have completed the installation of the PaddleX wheel package according to the [PaddleX Local Installation Guide](../../../installation/installation.en.md). If you wish to selectively install dependencies, please refer to the relevant instructions in the installation guide. The dependency group corresponding to this pipeline is `cv`.
#### 2.2.1 Command Line Experience
* You can quickly experience the instance segmentation pipeline effect with a single command. Use the [test file](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/general_instance_segmentation_004.png), and replace `--input` with the local path for prediction.
```bash
paddlex --pipeline instance_segmentation \
--input general_instance_segmentation_004.png \
--threshold 0.5 \
--save_path ./output \
--device gpu:0
```
The relevant parameter descriptions can be referred to in the parameter explanations in [2.2.2 Python Script Integration](). Supports specifying multiple devices simultaneously for parallel inference. For details, please refer to the documentation on pipeline parallel inference.
After running, the result will be printed to the terminal as follows:
```bash
{'res': {'input_path': 'general_instance_segmentation_004.png', 'page_index': None, 'boxes': [{'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'person', 'score': 0.8695873022079468, 'coordinate': [339.83426, 0, 639.8651, 575.22003]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'person', 'score': 0.8572642803192139, 'coordinate': [0.09976959, 0, 195.07274, 575.358]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'person', 'score': 0.8201770186424255, 'coordinate': [88.24664, 113.422424, 401.23077, 574.70197]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'person', 'score': 0.7110118269920349, 'coordinate': [522.54065, 21.457964, 767.5007, 574.2464]}, {'cls_id': 27, 'label': 'tie', 'score': 0.5543721914291382, 'coordinate': [247.38776, 312.4094, 355.2685, 574.1264]}], 'masks': '...'}}
```
The explanation of the result parameters can be referred to in [2.2.2 Python Script Integration](#222-python脚本方式集成).
The visualization results are saved under `save_path`, and the visualization results of instance segmentation are as follows:
 #### 2.2.2 Python Script Integration
* The above command line is for quickly experiencing and viewing the effect. Generally, in a project, it is often necessary to integrate through code. You can complete the quick inference of the pipeline with a few lines of code. The inference code is as follows:
```python
from paddlex import create_pipeline
pipeline = create_pipeline(pipeline="instance_segmentation")
output = pipeline.predict(input="general_instance_segmentation_004.png", threshold=0.5)
for res in output:
res.print()
res.save_to_img(save_path="./output/")
res.save_to_json(save_path="./output/")
```
In the above Python script, the following steps are performed:
(1) Instantiate the instance segmentation pipeline object through `create_pipeline()`, with specific parameter descriptions as follows:
#### 2.2.2 Python Script Integration
* The above command line is for quickly experiencing and viewing the effect. Generally, in a project, it is often necessary to integrate through code. You can complete the quick inference of the pipeline with a few lines of code. The inference code is as follows:
```python
from paddlex import create_pipeline
pipeline = create_pipeline(pipeline="instance_segmentation")
output = pipeline.predict(input="general_instance_segmentation_004.png", threshold=0.5)
for res in output:
res.print()
res.save_to_img(save_path="./output/")
res.save_to_json(save_path="./output/")
```
In the above Python script, the following steps are performed:
(1) Instantiate the instance segmentation pipeline object through `create_pipeline()`, with specific parameter descriptions as follows: