 通用语义分割产线中包含了语义分割模块,如您更考虑模型精度,请选择精度较高的模型,如您更考虑模型推理速度,请选择推理速度较快的模型,如您更考虑模型存储大小,请选择存储大小较小的模型。
通用语义分割产线中包含了语义分割模块,如您更考虑模型精度,请选择精度较高的模型,如您更考虑模型推理速度,请选择推理速度较快的模型,如您更考虑模型存储大小,请选择存储大小较小的模型。
| 模型 | 模型下载链接 | mloU(%) | GPU推理耗时(ms) | CPU推理耗时(ms) | 模型存储大小(M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deeplabv3_Plus-R50 | 推理模型/训练模型 | 80.36 | 61.0531 | 1513.58 | 94.9 M |
| Deeplabv3_Plus-R101 | 推理模型/训练模型 | 81.10 | 100.026 | 2460.71 | 162.5 M |
| Deeplabv3-R50 | 推理模型/训练模型 | 79.90 | 82.2631 | 1735.83 | 138.3 M |
| Deeplabv3-R101 | 推理模型/训练模型 | 80.85 | 121.492 | 2685.51 | 205.9 M |
| OCRNet_HRNet-W18 | 推理模型/训练模型 | 80.67 | 48.2335 | 906.385 | 43.1 M |
| OCRNet_HRNet-W48 | 推理模型/训练模型 | 82.15 | 78.9976 | 2226.95 | 249.8 M |
| PP-LiteSeg-T | 推理模型/训练模型 | 73.10 | 7.6827 | 138.683 | 28.5 M |
| PP-LiteSeg-B | 推理模型/训练模型 | 75.25 | 10.9935 | 194.727 | 47.0 M |
| SegFormer-B0 (slice) | 推理模型/训练模型 | 76.73 | 11.1946 | 268.929 | 13.2 M |
| SegFormer-B1 (slice) | 推理模型/训练模型 | 78.35 | 17.9998 | 403.393 | 48.5 M |
| SegFormer-B2 (slice) | 推理模型/训练模型 | 81.60 | 48.0371 | 1248.52 | 96.9 M |
| SegFormer-B3 (slice) | 推理模型/训练模型 | 82.47 | 64.341 | 1666.35 | 167.3 M |
| SegFormer-B4 (slice) | 推理模型/训练模型 | 82.38 | 82.4336 | 1995.42 | 226.7 M |
| SegFormer-B5 (slice) | 推理模型/训练模型 | 82.58 | 97.3717 | 2420.19 | 229.7 M |
注:以上精度指标为 Cityscapes 数据集 mloU。以上所有模型 GPU 推理耗时基于 NVIDIA Tesla T4 机器,精度类型为 FP32, CPU 推理速度基于 Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 5117 CPU @ 2.00GHz,线程数为8,精度类型为 FP32。
| 模型 | 模型下载链接 | mloU(%) | GPU推理耗时(ms) | CPU推理耗时(ms) | 模型存储大小(M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeaFormer_base(slice) | 推理模型/训练模型 | 40.92 | 24.4073 | 397.574 | 30.8 M |
| SeaFormer_large (slice) | 推理模型/训练模型 | 43.66 | 27.8123 | 550.464 | 49.8 M |
| SeaFormer_small (slice) | 推理模型/训练模型 | 38.73 | 19.2295 | 358.343 | 14.3 M |
| SeaFormer_tiny (slice) | 推理模型/训练模型 | 34.58 | 13.9496 | 330.132 | 6.1M |
注:以上精度指标为 ADE20k 数据集, slice 表示对输入图像进行了切图操作。以上所有模型 GPU 推理耗时基于 NVIDIA Tesla T4 机器,精度类型为 FP32, CPU 推理速度基于 Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 5117 CPU @ 2.00GHz,线程数为8,精度类型为 FP32。
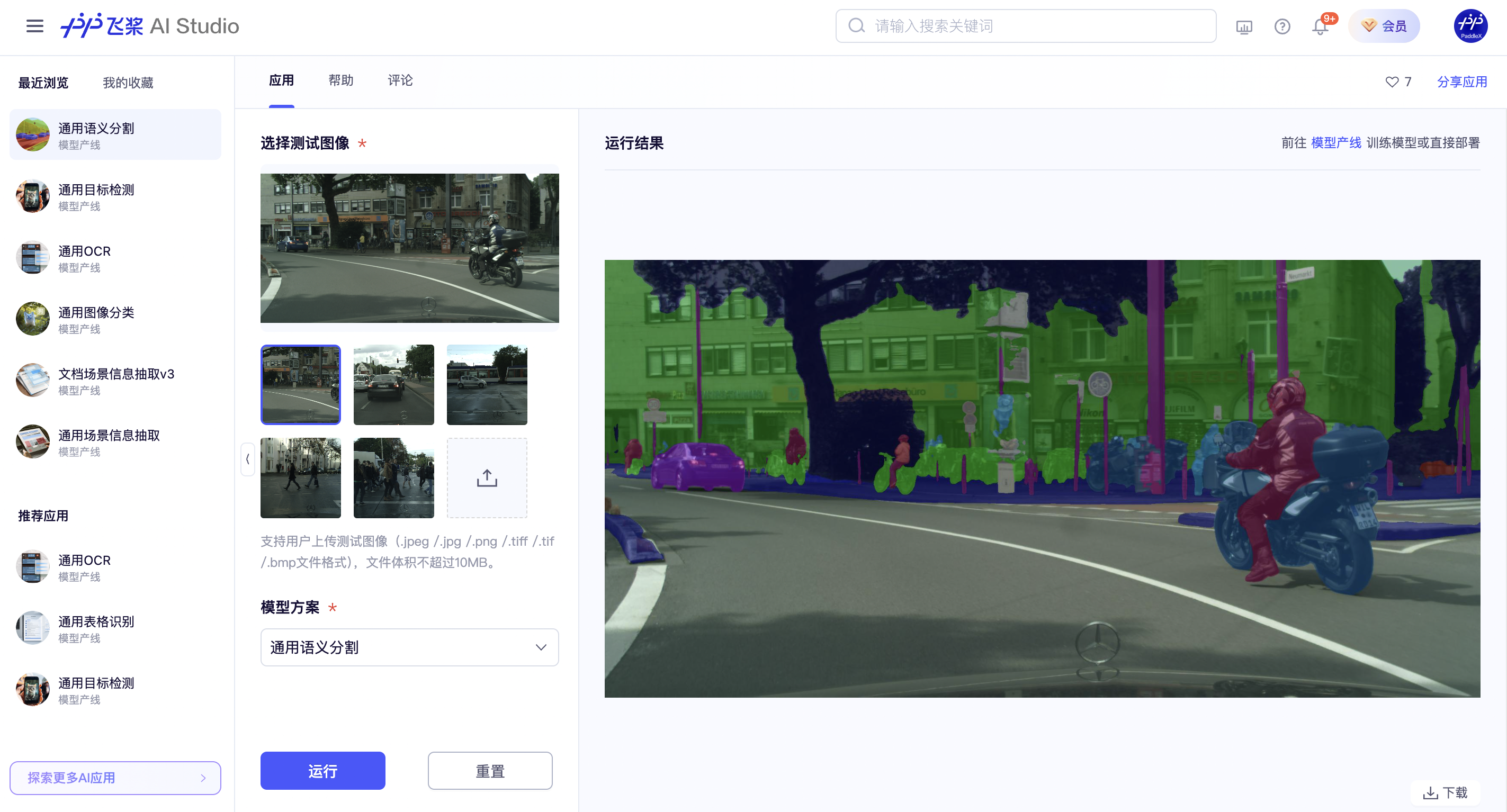 如果您对产线运行的效果满意,可以直接对产线进行集成部署,如果不满意,您也可以利用私有数据对产线中的模型进行在线微调。
### 2.2 本地体验
在本地使用通用语义分割产线前,请确保您已经按照[PaddleX本地安装教程](../../../installation/installation.md)完成了PaddleX的wheel包安装。
#### 2.2.1 命令行方式体验
一行命令即可快速体验语义分割产线效果,使用 [测试文件](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/PaddleX3.0/application/semantic_segmentation/makassaridn-road_demo.png),并将 `--input` 替换为本地路径,进行预测
```bash
paddlex --pipeline semantic_segmentation --input makassaridn-road_demo.png --device gpu:0
```
参数说明:
```
--pipeline:产线名称,此处为目标检测产线
--input:待处理的输入图片的本地路径或URL
--device 使用的GPU序号(例如gpu:0表示使用第0块GPU,gpu:1,2表示使用第1、2块GPU),也可选择使用CPU(--device cpu)
```
在执行上述 Python 脚本时,加载的是默认的语义分割产线配置文件,若您需要自定义配置文件,可执行如下命令获取:
如果您对产线运行的效果满意,可以直接对产线进行集成部署,如果不满意,您也可以利用私有数据对产线中的模型进行在线微调。
### 2.2 本地体验
在本地使用通用语义分割产线前,请确保您已经按照[PaddleX本地安装教程](../../../installation/installation.md)完成了PaddleX的wheel包安装。
#### 2.2.1 命令行方式体验
一行命令即可快速体验语义分割产线效果,使用 [测试文件](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/PaddleX3.0/application/semantic_segmentation/makassaridn-road_demo.png),并将 `--input` 替换为本地路径,进行预测
```bash
paddlex --pipeline semantic_segmentation --input makassaridn-road_demo.png --device gpu:0
```
参数说明:
```
--pipeline:产线名称,此处为目标检测产线
--input:待处理的输入图片的本地路径或URL
--device 使用的GPU序号(例如gpu:0表示使用第0块GPU,gpu:1,2表示使用第1、2块GPU),也可选择使用CPU(--device cpu)
```
在执行上述 Python 脚本时,加载的是默认的语义分割产线配置文件,若您需要自定义配置文件,可执行如下命令获取:
paddlex --get_pipeline_config semantic_segmentation
执行后,语义分割产线配置文件将被保存在当前路径。若您希望自定义保存位置,可执行如下命令(假设自定义保存位置为 ./my_path ):
paddlex --get_pipeline_config semantic_segmentation --save_path ./my_path
获取产线配置文件后,可将 --pipeline 替换为配置文件保存路径,即可使配置文件生效。例如,若配置文件保存路径为 ./semantic_segmentation.yaml,只需执行:
paddlex --pipeline ./semantic_segmentation.yaml --input makassaridn-road_demo.png --device gpu:0
其中,--model、--device 等参数无需指定,将使用配置文件中的参数。若依然指定了参数,将以指定的参数为准。
 可视化图片默认不进行保存,您可以通过 `--save_path` 自定义保存路径,随后所有结果将被保存在指定路径下。
#### 2.2.2 Python脚本方式集成
几行代码即可完成产线的快速推理,以通用语义分割产线为例:
```python
from paddlex import create_pipeline
pipeline = create_pipeline(pipeline="semantic_segmentation")
output = pipeline.predict("makassaridn-road_demo.png")
for res in output:
res.print() ## 打印预测的结构化输出
res.save_to_img("./output/") ## 保存结果可视化图像
res.save_to_json("./output/") ## 保存预测的结构化输出
```
得到的结果与命令行方式相同。
在上述 Python 脚本中,执行了如下几个步骤:
(1)实例化 `create_pipeline` 实例化产线对象:具体参数说明如下:
可视化图片默认不进行保存,您可以通过 `--save_path` 自定义保存路径,随后所有结果将被保存在指定路径下。
#### 2.2.2 Python脚本方式集成
几行代码即可完成产线的快速推理,以通用语义分割产线为例:
```python
from paddlex import create_pipeline
pipeline = create_pipeline(pipeline="semantic_segmentation")
output = pipeline.predict("makassaridn-road_demo.png")
for res in output:
res.print() ## 打印预测的结构化输出
res.save_to_img("./output/") ## 保存结果可视化图像
res.save_to_json("./output/") ## 保存预测的结构化输出
```
得到的结果与命令行方式相同。
在上述 Python 脚本中,执行了如下几个步骤:
(1)实例化 `create_pipeline` 实例化产线对象:具体参数说明如下:
| 参数 | 参数说明 | 参数类型 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
pipeline |
产线名称或是产线配置文件路径。如为产线名称,则必须为 PaddleX 所支持的产线。 | str |
无 |
device |
产线模型推理设备。支持:“gpu”,“cpu”。 | str |
gpu |
enable_hpi |
是否启用高性能推理,仅当该产线支持高性能推理时可用。 | bool |
False |
| 参数类型 | 参数说明 |
|---|---|
| Python Var | 支持直接传入Python变量,如numpy.ndarray表示的图像数据。 |
| str | 支持传入待预测数据文件路径,如图像文件的本地路径:/root/data/img.jpg。 |
| str | 支持传入待预测数据文件URL,如图像文件的网络URL:示例。 |
| str | 支持传入本地目录,该目录下需包含待预测数据文件,如本地路径:/root/data/。 |
| dict | 支持传入字典类型,字典的key需与具体任务对应,如图像分类任务对应\"img\",字典的val支持上述类型数据,例如:{\"img\": \"/root/data1\"}。 |
| list | 支持传入列表,列表元素需为上述类型数据,如[numpy.ndarray, numpy.ndarray],[\"/root/data/img1.jpg\", \"/root/data/img2.jpg\"],[\"/root/data1\", \"/root/data2\"],[{\"img\": \"/root/data1\"}, {\"img\": \"/root/data2/img.jpg\"}]。 |
| 方法 | 说明 | 方法参数 |
|---|---|---|
| 打印结果到终端 | - format_json:bool类型,是否对输出内容进行使用json缩进格式化,默认为True;- indent:int类型,json格式化设置,仅当format_json为True时有效,默认为4;- ensure_ascii:bool类型,json格式化设置,仅当format_json为True时有效,默认为False; |
|
| save_to_json | 将结果保存为json格式的文件 | - save_path:str类型,保存的文件路径,当为目录时,保存文件命名与输入文件类型命名一致;- indent:int类型,json格式化设置,默认为4;- ensure_ascii:bool类型,json格式化设置,默认为False; |
| save_to_img | 将结果保存为图像格式的文件 | - save_path:str类型,保存的文件路径,当为目录时,保存文件命名与输入文件类型命名一致; |
对于服务提供的主要操作:
200,响应体的属性如下:| 名称 | 类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
errorCode |
integer |
错误码。固定为0。 |
errorMsg |
string |
错误说明。固定为"Success"。 |
响应体还可能有result属性,类型为object,其中存储操作结果信息。
| 名称 | 类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
errorCode |
integer |
错误码。与响应状态码相同。 |
errorMsg |
string |
错误说明。 |
服务提供的主要操作如下:
infer对图像进行语义分割。
POST /semantic-segmentation
| 名称 | 类型 | 含义 | 是否必填 |
|---|---|---|---|
image |
string |
服务可访问的图像文件的URL或图像文件内容的Base64编码结果。 | 是 |
result具有如下属性:| 名称 | 类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
labelMap |
array |
记录图像中每个像素的类别标签(按照行优先顺序排列)。 |
size |
array |
图像形状。数组中元素依次为图像的高度和宽度。 |
image |
string |
语义分割结果图。图像为JPEG格式,使用Base64编码。 |
result示例如下:
{
"labelMap": [
0,
0,
1,
2
],
"size": [
2,
2
],
"image": "xxxxxx"
}
import base64
import requests
API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/semantic-segmentation" # 服务URL
image_path = "./demo.jpg"
output_image_path = "./out.jpg"
# 对本地图像进行Base64编码
with open(image_path, "rb") as file:
image_bytes = file.read()
image_data = base64.b64encode(image_bytes).decode("ascii")
payload = {"image": image_data} # Base64编码的文件内容或者图像URL
# 调用API
response = requests.post(API_URL, json=payload)
# 处理接口返回数据
assert response.status_code == 200
result = response.json()["result"]
with open(output_image_path, "wb") as file:
file.write(base64.b64decode(result["image"]))
print(f"Output image saved at {output_image_path}")
# result.labelMap 记录图像中每个像素的类别标签(按照行优先顺序排列)详见API参考文档
#include <iostream>
#include "cpp-httplib/httplib.h" // https://github.com/Huiyicc/cpp-httplib
#include "nlohmann/json.hpp" // https://github.com/nlohmann/json
#include "base64.hpp" // https://github.com/tobiaslocker/base64
int main() {
httplib::Client client("localhost:8080");
const std::string imagePath = "./demo.jpg";
const std::string outputImagePath = "./out.jpg";
httplib::Headers headers = {
{"Content-Type", "application/json"}
};
// 对本地图像进行Base64编码
std::ifstream file(imagePath, std::ios::binary | std::ios::ate);
std::streamsize size = file.tellg();
file.seekg(0, std::ios::beg);
std::vector<char> buffer(size);
if (!file.read(buffer.data(), size)) {
std::cerr << "Error reading file." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
std::string bufferStr(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(buffer.data()), buffer.size());
std::string encodedImage = base64::to_base64(bufferStr);
nlohmann::json jsonObj;
jsonObj["image"] = encodedImage;
std::string body = jsonObj.dump();
// 调用API
auto response = client.Post("/semantic-segmentation", headers, body, "application/json");
// 处理接口返回数据
if (response && response->status == 200) {
nlohmann::json jsonResponse = nlohmann::json::parse(response->body);
auto result = jsonResponse["result"];
encodedImage = result["image"];
std::string decodedString = base64::from_base64(encodedImage);
std::vector<unsigned char> decodedImage(decodedString.begin(), decodedString.end());
std::ofstream outputImage(outPutImagePath, std::ios::binary | std::ios::out);
if (outputImage.is_open()) {
outputImage.write(reinterpret_cast<char*>(decodedImage.data()), decodedImage.size());
outputImage.close();
std::cout << "Output image saved at " << outPutImagePath << std::endl;
// result.labelMap 记录图像中每个像素的类别标签(按照行优先顺序排列)详见API参考文档
} else {
std::cerr << "Unable to open file for writing: " << outPutImagePath << std::endl;
}
} else {
std::cout << "Failed to send HTTP request." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
import okhttp3.*;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.ObjectNode;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Base64;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/semantic-segmentation"; // 服务URL
String imagePath = "./demo.jpg"; // 本地图像
String outputImagePath = "./out.jpg"; // 输出图像
// 对本地图像进行Base64编码
File file = new File(imagePath);
byte[] fileContent = java.nio.file.Files.readAllBytes(file.toPath());
String imageData = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(fileContent);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
ObjectNode params = objectMapper.createObjectNode();
params.put("image", imageData); // Base64编码的文件内容或者图像URL
// 创建 OkHttpClient 实例
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
MediaType JSON = MediaType.Companion.get("application/json; charset=utf-8");
RequestBody body = RequestBody.Companion.create(params.toString(), JSON);
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(API_URL)
.post(body)
.build();
// 调用API并处理接口返回数据
try (Response response = client.newCall(request).execute()) {
if (response.isSuccessful()) {
String responseBody = response.body().string();
JsonNode resultNode = objectMapper.readTree(responseBody);
JsonNode result = resultNode.get("result");
String base64Image = result.get("image").asText();
JsonNode labelMap = result.get("labelMap");
byte[] imageBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(base64Image);
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(outputImagePath)) {
fos.write(imageBytes);
}
System.out.println("Output image saved at " + outputImagePath);
// result.labelMap 记录图像中每个像素的类别标签(按照行优先顺序排列)详见API参考文档
} else {
System.err.println("Request failed with code: " + response.code());
}
}
}
}
package main
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
API_URL := "http://localhost:8080/semantic-segmentation"
imagePath := "./demo.jpg"
outputImagePath := "./out.jpg"
// 对本地图像进行Base64编码
imageBytes, err := ioutil.ReadFile(imagePath)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error reading image file:", err)
return
}
imageData := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(imageBytes)
payload := map[string]string{"image": imageData} // Base64编码的文件内容或者图像URL
payloadBytes, err := json.Marshal(payload)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error marshaling payload:", err)
return
}
// 调用API
client := &http.Client{}
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", API_URL, bytes.NewBuffer(payloadBytes))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error creating request:", err)
return
}
res, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error sending request:", err)
return
}
defer res.Body.Close()
// 处理接口返回数据
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error reading response body:", err)
return
}
type Response struct {
Result struct {
Image string `json:"image"`
Labelmap []map[string]interface{} `json:"labelMap"`
} `json:"result"`
}
var respData Response
err = json.Unmarshal([]byte(string(body)), &respData)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error unmarshaling response body:", err)
return
}
outputImageData, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(respData.Result.Image)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error decoding base64 image data:", err)
return
}
err = ioutil.WriteFile(outputImagePath, outputImageData, 0644)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error writing image to file:", err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("Image saved at %s.jpg\n", outputImagePath)
// result.labelMap 记录图像中每个像素的类别标签(按照行优先顺序排列)详见API参考文档
}
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Net.Http.Headers;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Newtonsoft.Json.Linq;
class Program
{
static readonly string API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/semantic-segmentation";
static readonly string imagePath = "./demo.jpg";
static readonly string outputImagePath = "./out.jpg";
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
var httpClient = new HttpClient();
// 对本地图像进行Base64编码
byte[] imageBytes = File.ReadAllBytes(imagePath);
string image_data = Convert.ToBase64String(imageBytes);
var payload = new JObject{ { "image", image_data } }; // Base64编码的文件内容或者图像URL
var content = new StringContent(payload.ToString(), Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
// 调用API
HttpResponseMessage response = await httpClient.PostAsync(API_URL, content);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
// 处理接口返回数据
string responseBody = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
JObject jsonResponse = JObject.Parse(responseBody);
string base64Image = jsonResponse["result"]["image"].ToString();
byte[] outputImageBytes = Convert.FromBase64String(base64Image);
File.WriteAllBytes(outputImagePath, outputImageBytes);
Console.WriteLine($"Output image saved at {outputImagePath}");
// result.labelMap 记录图像中每个像素的类别标签(按照行优先顺序排列)详见API参考文档
}
}
const axios = require('axios');
const fs = require('fs');
const API_URL = 'http://localhost:8080/semantic-segmentation'
const imagePath = './demo.jpg'
const outputImagePath = "./out.jpg";
let config = {
method: 'POST',
maxBodyLength: Infinity,
url: API_URL,
data: JSON.stringify({
'image': encodeImageToBase64(imagePath) // Base64编码的文件内容或者图像URL
})
};
// 对本地图像进行Base64编码
function encodeImageToBase64(filePath) {
const bitmap = fs.readFileSync(filePath);
return Buffer.from(bitmap).toString('base64');
}
// 调用API
axios.request(config)
.then((response) => {
// 处理接口返回数据
const result = response.data["result"];
const imageBuffer = Buffer.from(result["image"], 'base64');
fs.writeFile(outputImagePath, imageBuffer, (err) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(`Output image saved at ${outputImagePath}`);
});
// result.labelMap 记录图像中每个像素的类别标签(按照行优先顺序排列)详见API参考文档
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log(error);
});
<?php
$API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/semantic-segmentation"; // 服务URL
$image_path = "./demo.jpg";
$output_image_path = "./out.jpg";
// 对本地图像进行Base64编码
$image_data = base64_encode(file_get_contents($image_path));
$payload = array("image" => $image_data); // Base64编码的文件内容或者图像URL
// 调用API
$ch = curl_init($API_URL);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, json_encode($payload));
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, array('Content-Type: application/json'));
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
$response = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
// 处理接口返回数据
$result = json_decode($response, true)["result"];
file_put_contents($output_image_path, base64_decode($result["image"]));
echo "Output image saved at " . $output_image_path . "\n";
// result.labelMap 记录图像中每个像素的类别标签(按照行优先顺序排列)详见API参考文档
?>