---
comments: true
---
# PaddleX Image Feature Task Module Data Annotation Tutorial
This section will introduce how to use the [Labelme](https://github.com/wkentaro/labelme) annotation tool to complete data annotation for image feature-related single models.
Click the link above to install the data annotation tool and view detailed usage instructions by referring to the homepage documentation.
## 1. Labelme Annotation
### 1.1 Introduction to Labelme Annotation Tool
`Labelme` is a Python-based image annotation software with a graphical user interface. It can be used for tasks such as image classification, object detection, and image segmentation. In image feature annotation tasks, labels are stored as `JSON` files.
### 1.2 Labelme Installation
To avoid environment conflicts, it is recommended to install in a `conda` environment.
```bash
conda create -n labelme python=3.10
conda activate labelme
pip install pyqt5
pip install labelme
```
### 1.3 Labelme Annotation Process
#### 1.3.1 Prepare Data for Annotation
* Create a root directory for the dataset, e.g., `pets`.
* Create an `images` directory (must be named `images`) within `pets` and store the images to be annotated in the `images` directory, as shown below:
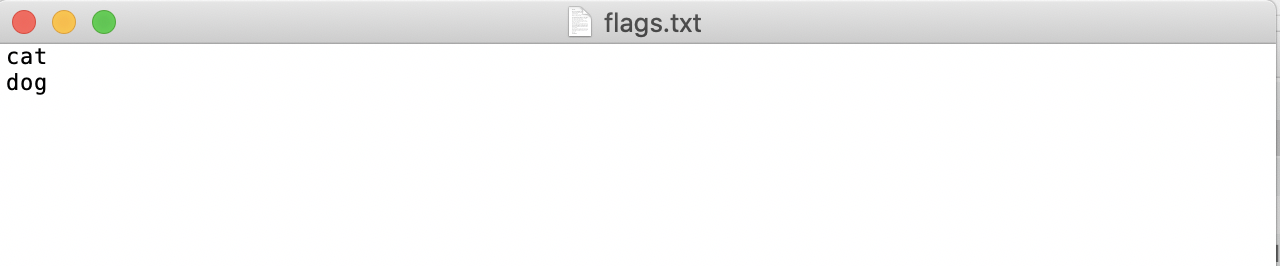
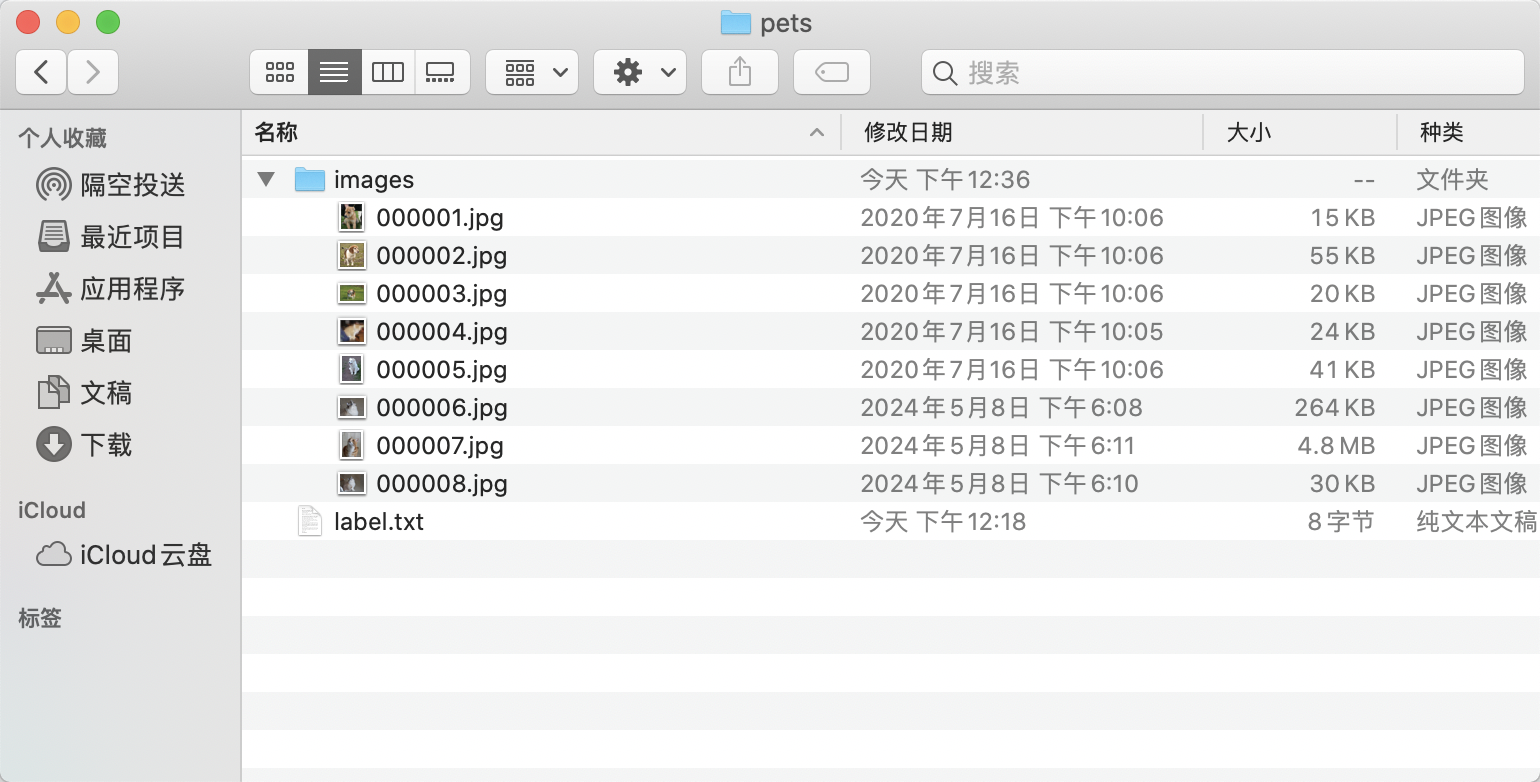 * Create a category label file `flags.txt` in the `pets` folder for the dataset to be annotated, and write the categories of the dataset to be annotated into `flags.txt` line by line. Taking the `flags.txt` for a cat-dog classification dataset as an example, as shown below:
* Create a category label file `flags.txt` in the `pets` folder for the dataset to be annotated, and write the categories of the dataset to be annotated into `flags.txt` line by line. Taking the `flags.txt` for a cat-dog classification dataset as an example, as shown below:
 #### 1.3.2 Start Labelme
Navigate to the root directory of the dataset to be annotated in the terminal and start the `labelme` annotation tool.
```bash
cd path/to/pets
labelme images --nodata --autosave --output annotations --flags flags.txt
```
* `flags` creates classification labels for images, passing in the label path.
* `nodata` stops storing image data in JSON files.
* `autosave` enables automatic saving.
* `output` specifies the storage path for label files.
#### 1.3.3 Start Image Annotation
* After starting `labelme`, it will look like this:
#### 1.3.2 Start Labelme
Navigate to the root directory of the dataset to be annotated in the terminal and start the `labelme` annotation tool.
```bash
cd path/to/pets
labelme images --nodata --autosave --output annotations --flags flags.txt
```
* `flags` creates classification labels for images, passing in the label path.
* `nodata` stops storing image data in JSON files.
* `autosave` enables automatic saving.
* `output` specifies the storage path for label files.
#### 1.3.3 Start Image Annotation
* After starting `labelme`, it will look like this:
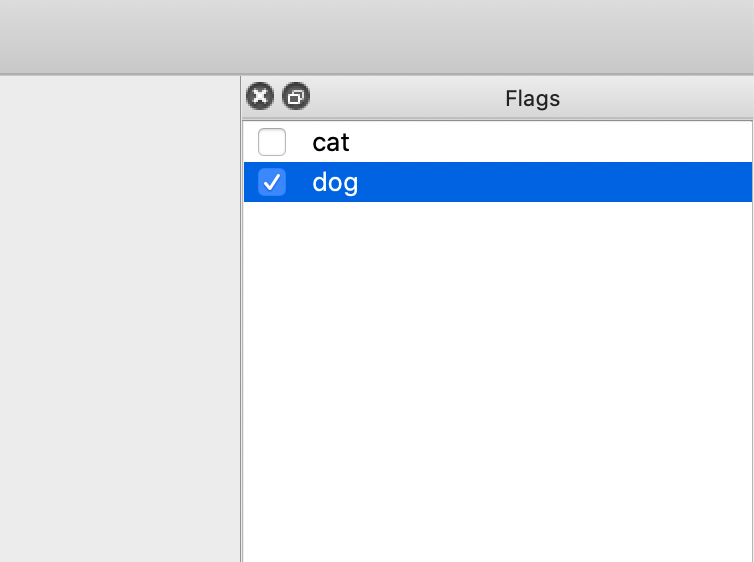
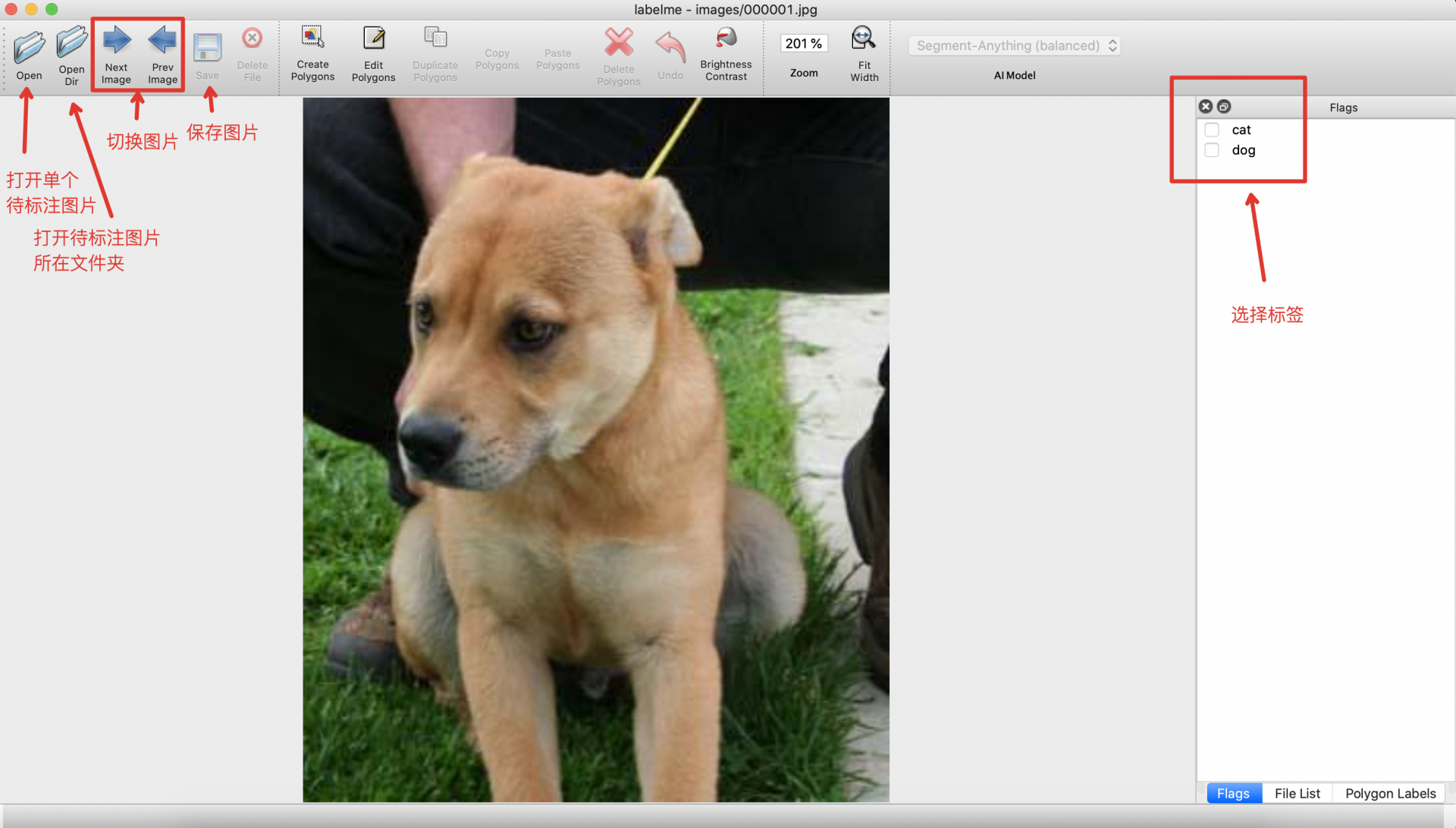 * Select the category in the `Flags` interface.
* Select the category in the `Flags` interface.
 * After annotation, click Save. (If `output` is not specified when starting `labelme`, it will prompt to select the save path upon the first save. If `autosave` is enabled, there is no need to click the Save button).
* After annotation, click Save. (If `output` is not specified when starting `labelme`, it will prompt to select the save path upon the first save. If `autosave` is enabled, there is no need to click the Save button).
 * Then click `Next Image` to annotate the next image.
* Then click `Next Image` to annotate the next image.
 * After annotating all images, use the [convert_to_imagenet.py](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/PaddleX3.0/doc_images/applications/image_classification_dataset_prepare/convert_to_imagenet.py) to convert the annotated dataset to `ImageNet-1k` dataset format, generating `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `label.txt`.
```bash
python convert_to_imagenet.py --dataset_path /path/to/dataset
```
`dataset_path` is the annotated `labelme` format classification dataset.
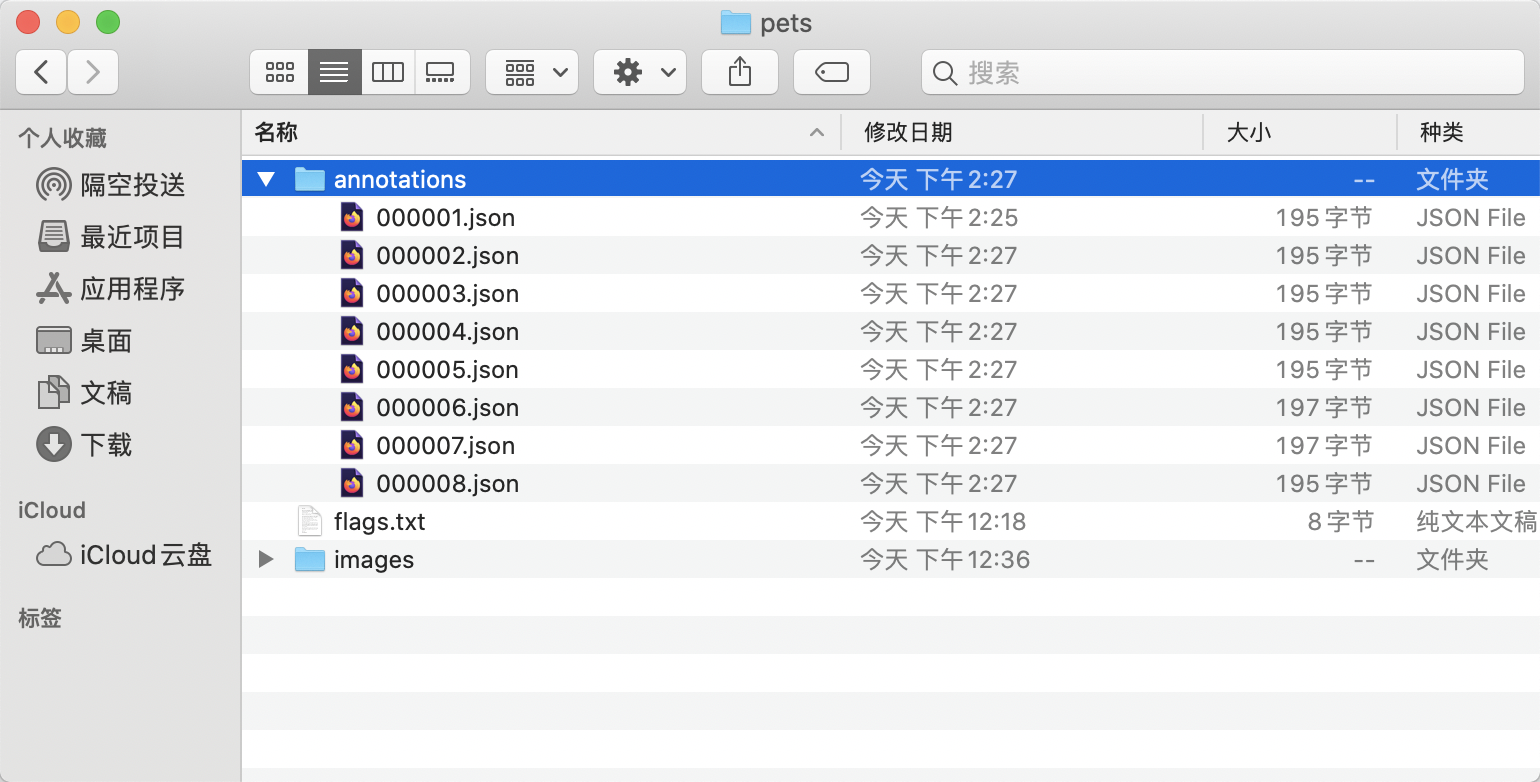
* The final directory structure after organization is as follows:
* After annotating all images, use the [convert_to_imagenet.py](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/PaddleX3.0/doc_images/applications/image_classification_dataset_prepare/convert_to_imagenet.py) to convert the annotated dataset to `ImageNet-1k` dataset format, generating `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `label.txt`.
```bash
python convert_to_imagenet.py --dataset_path /path/to/dataset
```
`dataset_path` is the annotated `labelme` format classification dataset.
* The final directory structure after organization is as follows:
 #### 1.3.4 Data Format Conversion
After obtaining data in `LabelMe` format, the data format needs to be converted to `ShiTuRecDataset` format. Below is a code example that demonstrates how to convert the data labeled using `LabelMe` according to the previous tutorial.
```bash
# Download and unzip the LabelMe format example dataset
cd /path/to/paddlex
wget https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/data/image_classification_labelme_examples.tar -P ./dataset
tar -xf ./dataset/image_classification_labelme_examples.tar -C ./dataset/
# Convert the LabelMe example dataset
python main.py -c paddlex/configs/general_recognition/PP-ShiTuV2_rec.yaml \
-o Global.mode=check_dataset \
-o Global.dataset_dir=./dataset/image_classification_labelme_examples \
-o CheckDataset.convert.enable=True \
-o CheckDataset.convert.src_dataset_type=LabelMe
```
## 3. Data Format
The dataset defined by PaddleX for image classification tasks is named ShiTuRecDataset, with the following organizational structure and annotation format:
```bash
dataset_dir # Root directory of the dataset, the directory name can be changed
├── images # Directory where images are saved, the directory name can be changed, but should correspond to the content of train.txt, query.txt, gallery.txt
├── gallery.txt # Annotation file for the gallery set, the file name cannot be changed. Each line gives the path of the image to be retrieved and its feature label, separated by a space. Example: images/WOMEN/Blouses_Shirts/id_00000001/02_2_side.jpg 3997
└── query.txt # Annotation file for the query set, the file name cannot be changed. Each line gives the path of the database image and its feature label, separated by a space. Example: images/WOMEN/Blouses_Shirts/id_00000001/02_1_front.jpg 3997
```
The annotation files use an image feature format. Please refer to the above specifications to prepare your data. Additionally, you can refer to the [example dataset](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/data/Inshop_examples.tar).
#### 1.3.4 Data Format Conversion
After obtaining data in `LabelMe` format, the data format needs to be converted to `ShiTuRecDataset` format. Below is a code example that demonstrates how to convert the data labeled using `LabelMe` according to the previous tutorial.
```bash
# Download and unzip the LabelMe format example dataset
cd /path/to/paddlex
wget https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/data/image_classification_labelme_examples.tar -P ./dataset
tar -xf ./dataset/image_classification_labelme_examples.tar -C ./dataset/
# Convert the LabelMe example dataset
python main.py -c paddlex/configs/general_recognition/PP-ShiTuV2_rec.yaml \
-o Global.mode=check_dataset \
-o Global.dataset_dir=./dataset/image_classification_labelme_examples \
-o CheckDataset.convert.enable=True \
-o CheckDataset.convert.src_dataset_type=LabelMe
```
## 3. Data Format
The dataset defined by PaddleX for image classification tasks is named ShiTuRecDataset, with the following organizational structure and annotation format:
```bash
dataset_dir # Root directory of the dataset, the directory name can be changed
├── images # Directory where images are saved, the directory name can be changed, but should correspond to the content of train.txt, query.txt, gallery.txt
├── gallery.txt # Annotation file for the gallery set, the file name cannot be changed. Each line gives the path of the image to be retrieved and its feature label, separated by a space. Example: images/WOMEN/Blouses_Shirts/id_00000001/02_2_side.jpg 3997
└── query.txt # Annotation file for the query set, the file name cannot be changed. Each line gives the path of the database image and its feature label, separated by a space. Example: images/WOMEN/Blouses_Shirts/id_00000001/02_1_front.jpg 3997
```
The annotation files use an image feature format. Please refer to the above specifications to prepare your data. Additionally, you can refer to the [example dataset](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/data/Inshop_examples.tar).
 * Create a category label file `flags.txt` in the `pets` folder for the dataset to be annotated, and write the categories of the dataset to be annotated into `flags.txt` line by line. Taking the `flags.txt` for a cat-dog classification dataset as an example, as shown below:
* Create a category label file `flags.txt` in the `pets` folder for the dataset to be annotated, and write the categories of the dataset to be annotated into `flags.txt` line by line. Taking the `flags.txt` for a cat-dog classification dataset as an example, as shown below:
 #### 1.3.2 Start Labelme
Navigate to the root directory of the dataset to be annotated in the terminal and start the `labelme` annotation tool.
```bash
cd path/to/pets
labelme images --nodata --autosave --output annotations --flags flags.txt
```
* `flags` creates classification labels for images, passing in the label path.
* `nodata` stops storing image data in JSON files.
* `autosave` enables automatic saving.
* `output` specifies the storage path for label files.
#### 1.3.3 Start Image Annotation
* After starting `labelme`, it will look like this:
#### 1.3.2 Start Labelme
Navigate to the root directory of the dataset to be annotated in the terminal and start the `labelme` annotation tool.
```bash
cd path/to/pets
labelme images --nodata --autosave --output annotations --flags flags.txt
```
* `flags` creates classification labels for images, passing in the label path.
* `nodata` stops storing image data in JSON files.
* `autosave` enables automatic saving.
* `output` specifies the storage path for label files.
#### 1.3.3 Start Image Annotation
* After starting `labelme`, it will look like this:
 * Select the category in the `Flags` interface.
* Select the category in the `Flags` interface.
 * After annotation, click Save. (If `output` is not specified when starting `labelme`, it will prompt to select the save path upon the first save. If `autosave` is enabled, there is no need to click the Save button).
* After annotation, click Save. (If `output` is not specified when starting `labelme`, it will prompt to select the save path upon the first save. If `autosave` is enabled, there is no need to click the Save button).
 * Then click `Next Image` to annotate the next image.
* Then click `Next Image` to annotate the next image.
 * After annotating all images, use the [convert_to_imagenet.py](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/PaddleX3.0/doc_images/applications/image_classification_dataset_prepare/convert_to_imagenet.py) to convert the annotated dataset to `ImageNet-1k` dataset format, generating `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `label.txt`.
```bash
python convert_to_imagenet.py --dataset_path /path/to/dataset
```
`dataset_path` is the annotated `labelme` format classification dataset.
* The final directory structure after organization is as follows:
* After annotating all images, use the [convert_to_imagenet.py](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/PaddleX3.0/doc_images/applications/image_classification_dataset_prepare/convert_to_imagenet.py) to convert the annotated dataset to `ImageNet-1k` dataset format, generating `train.txt`, `val.txt`, and `label.txt`.
```bash
python convert_to_imagenet.py --dataset_path /path/to/dataset
```
`dataset_path` is the annotated `labelme` format classification dataset.
* The final directory structure after organization is as follows:
 #### 1.3.4 Data Format Conversion
After obtaining data in `LabelMe` format, the data format needs to be converted to `ShiTuRecDataset` format. Below is a code example that demonstrates how to convert the data labeled using `LabelMe` according to the previous tutorial.
```bash
# Download and unzip the LabelMe format example dataset
cd /path/to/paddlex
wget https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/data/image_classification_labelme_examples.tar -P ./dataset
tar -xf ./dataset/image_classification_labelme_examples.tar -C ./dataset/
# Convert the LabelMe example dataset
python main.py -c paddlex/configs/general_recognition/PP-ShiTuV2_rec.yaml \
-o Global.mode=check_dataset \
-o Global.dataset_dir=./dataset/image_classification_labelme_examples \
-o CheckDataset.convert.enable=True \
-o CheckDataset.convert.src_dataset_type=LabelMe
```
## 3. Data Format
The dataset defined by PaddleX for image classification tasks is named ShiTuRecDataset, with the following organizational structure and annotation format:
```bash
dataset_dir # Root directory of the dataset, the directory name can be changed
├── images # Directory where images are saved, the directory name can be changed, but should correspond to the content of train.txt, query.txt, gallery.txt
├── gallery.txt # Annotation file for the gallery set, the file name cannot be changed. Each line gives the path of the image to be retrieved and its feature label, separated by a space. Example: images/WOMEN/Blouses_Shirts/id_00000001/02_2_side.jpg 3997
└── query.txt # Annotation file for the query set, the file name cannot be changed. Each line gives the path of the database image and its feature label, separated by a space. Example: images/WOMEN/Blouses_Shirts/id_00000001/02_1_front.jpg 3997
```
The annotation files use an image feature format. Please refer to the above specifications to prepare your data. Additionally, you can refer to the [example dataset](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/data/Inshop_examples.tar).
#### 1.3.4 Data Format Conversion
After obtaining data in `LabelMe` format, the data format needs to be converted to `ShiTuRecDataset` format. Below is a code example that demonstrates how to convert the data labeled using `LabelMe` according to the previous tutorial.
```bash
# Download and unzip the LabelMe format example dataset
cd /path/to/paddlex
wget https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/data/image_classification_labelme_examples.tar -P ./dataset
tar -xf ./dataset/image_classification_labelme_examples.tar -C ./dataset/
# Convert the LabelMe example dataset
python main.py -c paddlex/configs/general_recognition/PP-ShiTuV2_rec.yaml \
-o Global.mode=check_dataset \
-o Global.dataset_dir=./dataset/image_classification_labelme_examples \
-o CheckDataset.convert.enable=True \
-o CheckDataset.convert.src_dataset_type=LabelMe
```
## 3. Data Format
The dataset defined by PaddleX for image classification tasks is named ShiTuRecDataset, with the following organizational structure and annotation format:
```bash
dataset_dir # Root directory of the dataset, the directory name can be changed
├── images # Directory where images are saved, the directory name can be changed, but should correspond to the content of train.txt, query.txt, gallery.txt
├── gallery.txt # Annotation file for the gallery set, the file name cannot be changed. Each line gives the path of the image to be retrieved and its feature label, separated by a space. Example: images/WOMEN/Blouses_Shirts/id_00000001/02_2_side.jpg 3997
└── query.txt # Annotation file for the query set, the file name cannot be changed. Each line gives the path of the database image and its feature label, separated by a space. Example: images/WOMEN/Blouses_Shirts/id_00000001/02_1_front.jpg 3997
```
The annotation files use an image feature format. Please refer to the above specifications to prepare your data. Additionally, you can refer to the [example dataset](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/data/Inshop_examples.tar).