| Model | Model Download Link |
Recognition Avg Accuracy (%) |
GPU Inference Time (ms) |
CPU Inference Time (ms) |
Model Storage Size (M) |
Introduction |
| PP-OCRv4_server_rec_doc | Inference Model/Training Model |
81.53 |
|
|
74.7 M |
PP-OCRv4_server_rec_doc is trained on a mixed dataset of more Chinese document data and PP-OCR training data, based on PP-OCRv4_server_rec. It enhances the recognition of traditional Chinese characters, Japanese, and special characters, supporting over 15,000 characters. It improves both document-related and general text recognition capabilities. |
| PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec | Inference Model/Training Model |
78.74 |
7.95018 |
46.7868 |
10.6 M |
The lightweight recognition model of PP-OCRv4, with high inference efficiency, suitable for deployment on various hardware devices, including edge devices |
| PP-OCRv4_server_rec | Inference Model/Training Model |
80.61 |
7.19439 |
140.179 |
71.2 M |
The server-side recognition model of PP-OCRv4, with high inference accuracy, suitable for deployment on various servers |
| en_PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec | Inference Model/Training Model |
70.39 |
|
|
6.8 M |
The ultra-lightweight English recognition model trained based on the PP-OCRv4 recognition model, supporting English and numeric recognition |
👉Model List Details
* Chinese Recognition Model
| Model | Model Download Link |
Recognition Avg Accuracy(%) |
GPU Inference Time (ms) |
CPU Inference Time (ms) |
Model Storage Size (M) |
Introduction |
| PP-OCRv4_server_rec_doc | Inference Model/Training Model |
|
|
|
|
PP-OCRv4_server_rec_doc is trained on a mixed dataset of more Chinese document data and PP-OCR training data based on PP-OCRv4_server_rec. It has added the recognition capabilities for some traditional Chinese characters, Japanese, and special characters. The number of recognizable characters is over 15,000. In addition to the improvement in document-related text recognition, it also enhances the general text recognition capability. |
| PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec | Inference Model/Training Model |
78.20 |
7.95018 |
46.7868 |
10.6 M |
The PP-OCRv4 recognition model is an upgrade from PP-OCRv3. Under comparable speed conditions, the effect in Chinese and English scenarios is further improved. The average recognition accuracy of the 80 multilingual models is increased by more than 8%. |
| PP-OCRv4_server_rec | Inference Model/Trained Model |
79.20 |
7.19439 |
140.179 |
71.2 M |
A high-precision server text recognition model, featuring high accuracy, fast speed, and multilingual support. It is suitable for text recognition tasks in various scenarios. |
| PP-OCRv3_mobile_rec | Inference Model/Training Model |
|
|
|
|
An ultra-lightweight OCR model suitable for mobile applications. It adopts an encoder-decoder structure based on Transformer and enhances recognition accuracy and efficiency through techniques such as data augmentation and mixed precision training. The model size is 10.6M, making it suitable for deployment on resource-constrained devices. It can be used in scenarios such as mobile photo translation and business card recognition. |
Note: The evaluation set for the above accuracy indicators is the Chinese dataset built by PaddleOCR, covering multiple scenarios such as street view, web images, documents, and handwriting. The text recognition includes 11,000 images. The GPU inference time for all models is based on NVIDIA Tesla T4 machines with FP32 precision type. The CPU inference speed is based on Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 5117 CPU @ 2.00GHz with 8 threads and FP32 precision type.
| Model | Model Download Link |
Recognition Avg Accuracy(%) |
GPU Inference Time (ms) |
CPU Inference Time |
Model Storage Size (M) |
Introduction |
| ch_SVTRv2_rec | Inference Model/Training Model |
68.81 |
8.36801 |
165.706 |
73.9 M |
SVTRv2 is a server text recognition model developed by the OpenOCR team of Fudan University's Visual and Learning Laboratory (FVL). It won the first prize in the PaddleOCR Algorithm Model Challenge - Task One: OCR End-to-End Recognition Task. The end-to-end recognition accuracy on the A list is 6% higher than that of PP-OCRv4.
|
Note: The evaluation set for the above accuracy indicators is the PaddleOCR Algorithm Model Challenge - Task One: OCR End-to-End Recognition Task A list. The GPU inference time for all models is based on NVIDIA Tesla T4 machines with FP32 precision type. The CPU inference speed is based on Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 5117 CPU @ 2.00GHz with 8 threads and FP32 precision type.
| Model | Model Download Link |
Recognition Avg Accuracy(%) |
GPU Inference Time (ms) |
CPU Inference Time |
Model Storage Size (M) |
Introduction |
| ch_RepSVTR_rec | Inference Model/Training Model |
65.07 |
10.5047 |
51.5647 |
22.1 M |
The RepSVTR text recognition model is a mobile text recognition model based on SVTRv2. It won the first prize in the PaddleOCR Algorithm Model Challenge - Task One: OCR End-to-End Recognition Task. The end-to-end recognition accuracy on the B list is 2.5% higher than that of PP-OCRv4, with the same inference speed. |
Note: The evaluation set for the above accuracy indicators is the PaddleOCR Algorithm Model Challenge - Task One: OCR End-to-End Recognition Task B list. The GPU inference time for all models is based on NVIDIA Tesla T4 machines with FP32 precision type. The CPU inference speed is based on Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 5117 CPU @ 2.00GHz with 8 threads and FP32 precision type.
* English Recognition Model
| Model | Model Download Link |
Recognition Avg Accuracy(%) |
GPU Inference Time (ms) |
CPU Inference Time |
Model Storage Size (M) |
Introduction |
| en_PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec | Inference Model/Training Model |
|
|
|
|
[Latest] Further upgraded based on PP-OCRv3, with improved accuracy under comparable speed conditions. |
| en_PP-OCRv3_mobile_rec | Inference Model/Training Model |
|
|
|
|
Ultra-lightweight model, supporting English and numeric recognition. |
* Multilingual Recognition Model
| Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Options |
Default Value |
input |
Data to be predicted, supports multiple input types (required). |
Python Var|str|list |
- Python Var: Image data represented by
numpy.ndarray
- str: Local path of an image file or PDF file, e.g.,
/root/data/img.jpg; URL link, e.g., network URL of an image file or PDF file: example; local directory, which must contain images to be predicted, e.g., /root/data/ (prediction of PDF files in directories is currently not supported; PDF files must specify the exact file path)
- List: Elements of the list must be of the above types, e.g.,
[numpy.ndarray, numpy.ndarray], ["/root/data/img1.jpg", "/root/data/img2.jpg"], ["/root/data1", "/root/data2"]
|
None |
device |
The device used for inference. |
str|None |
- CPU: Use CPU for inference, e.g.,
cpu
- GPU: Use the first GPU for inference, e.g.,
gpu:0
- NPU: Use the first NPU for inference, e.g.,
npu:0
- XPU: Use the first XPU for inference, e.g.,
xpu:0
- MLU: Use the first MLU for inference, e.g.,
mlu:0
- DCU: Use the first DCU for inference, e.g.,
dcu:0
- None: If set to
None, the default value from the production line initialization will be used. During initialization, the local GPU 0 will be used if available; otherwise, the CPU will be used.
|
None |
use_doc_orientation_classify |
Whether to use the document orientation classification module. |
bool|None |
- bool:
True or False
- None: If set to
None, the default value from the production line initialization will be used, which is True
|
None |
use_doc_unwarping |
Whether to use the document unwarping module. |
bool|None |
- bool:
True or False
- None: If set to
None, the default value from the production line initialization will be used, which is True
|
None |
use_textline_orientation |
Whether to use the text line orientation classification module. |
bool|None |
- bool:
True or False
- None: If set to
None, the default value from the production line initialization will be used, which is True
|
None |
text_det_limit_side_len |
The limit on the side length of the image for text detection. |
int|None |
- int: Any integer greater than
0
- None: If set to
None, the default value from the production line initialization will be used, which is 960
|
None |
text_det_limit_type |
The type of limit on the side length of the image for text detection. |
str|None |
- str: Supports
min and max. min ensures that the shortest side of the image is not less than det_limit_side_len, while max ensures that the longest side is not greater than limit_side_len
- None: If set to
None, the default value from the production line initialization will be used, which is max
|
None |
text_det_thresh |
The detection pixel threshold. Pixels with scores greater than this threshold in the output probability map will be considered as text pixels. |
float|None |
- float: Any floating-point number greater than
0
- None: If set to
None, the default value from the production line initialization will be used, which is 0.3
|
None |
text_det_box_thresh |
The detection box threshold. A detection result will be considered as a text region if the average score of all pixels within the bounding box is greater than this threshold. |
float|None |
- float: Any floating-point number greater than
0
- None: If set to
None, the default value from the production line initialization will be used, which is 0.6
|
None |
text_det_unclip_ratio |
The text detection expansion ratio. The larger this value, the larger the expanded area. |
float|None |
- float: Any floating-point number greater than
0
- None: If set to
None, the default value from the production line initialization will be used, which is 2.0
|
None |
text_rec_score_thresh |
The text recognition score threshold. Text results with scores greater than this threshold will be retained. |
float|None |
- float: Any floating-point number greater than
0
- None: If set to
None, the default value from the production line initialization will be used, which is 0.0 (i.e., no threshold)
|
None |
(3) Process the prediction results. The prediction result for each sample is of type `dict`, and supports operations such as printing, saving as an image, and saving as a `json` file:
| Method |
Description |
Parameter |
Parameter Type |
Parameter Description |
Default Value |
print() |
Print the result to the terminal |
format_json |
bool |
Whether to format the output content using JSON indentation |
True |
indent |
int |
Specify the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable. This is only effective when format_json is True |
4 |
ensure_ascii |
bool |
Control whether non-ASCII characters are escaped to Unicode. When set to True, all non-ASCII characters will be escaped; False retains the original characters. This is only effective when format_json is True |
False |
save_to_json() |
Save the result as a JSON file |
save_path |
str |
The file path for saving. When a directory is specified, the saved file name will match the input file name |
None |
indent |
int |
Specify the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable. This is only effective when format_json is True |
4 |
ensure_ascii |
bool |
Control whether non-ASCII characters are escaped to Unicode. When set to True, all non-ASCII characters will be escaped; False retains the original characters. This is only effective when format_json is True |
False |
save_to_img() |
Save the result as an image file |
save_path |
str |
The file path for saving, supporting both directory and file paths |
None |
- Calling the `print()` method will print the result to the terminal. The printed content is explained as follows:
- `input_path`: `(str)` The input path of the image to be predicted
- `model_settings`: `(Dict[str, bool])` The model parameters required for the production line configuration
- `use_doc_preprocessor`: `(bool)` Controls whether to enable the document preprocessing sub-line
- `use_textline_orientation`: `(bool)` Controls whether to enable text line orientation classification
- `doc_preprocessor_res`: `(Dict[str, Union[str, Dict[str, bool], int]])` The output result of the document preprocessing sub-line. This exists only when `use_doc_preprocessor=True`
- `input_path`: `(Union[str, None])` The image path accepted by the preprocessing sub-line. When the input is `numpy.ndarray`, it is saved as `None`
- `model_settings`: `(Dict)` The model configuration parameters for the preprocessing sub-line
- `use_doc_orientation_classify`: `(bool)` Controls whether to enable document orientation classification
- `use_doc_unwarping`: `(bool)` Controls whether to enable document unwarping
- `angle`: `(int)` The prediction result of document orientation classification. When enabled, it takes values [0,1,2,3], corresponding to [0°,90°,180°,270°]; when disabled, it is -1
- `dt_polys`: `(List[numpy.ndarray])` A list of polygon boxes for text detection. Each detection box is represented by a numpy array of 4 vertex coordinates, with a shape of (4, 2) and data type int16
- `dt_scores`: `(List[float])` A list of confidence scores for text detection boxes
- `text_det_params`: `(Dict[str, Dict[str, int, float]])` The configuration parameters for the text detection module
- `limit_side_len`: `(int)` The side length limit value for image preprocessing
- `limit_type`: `(str)` The processing method for side length limits
- `thresh`: `(float)` The confidence threshold for text pixel classification
- `box_thresh`: `(float)` The confidence threshold for text detection boxes
- `unclip_ratio`: `(float)` The expansion ratio for text detection boxes
- `text_type`: `(str)` The type of text detection, currently fixed as "general"
- `textline_orientation_angles`: `(List[int])` The prediction results for text line orientation classification. When enabled, it returns actual angle values (e.g., [0,0,1]); when disabled, it returns [-1,-1,-1]
- `text_rec_score_thresh`: `(float)` The filtering threshold for text recognition results
- `rec_texts`: `(List[str])` A list of text recognition results, containing only texts with confidence scores above `text_rec_score_thresh`
- `rec_scores`: `(List[float])` A list of confidence scores for text recognition, filtered by `text_rec_score_thresh`
- `rec_polys`: `(List[numpy.ndarray])` A list of text detection boxes filtered by confidence score, in the same format as `dt_polys`
- `rec_boxes`: `(numpy.ndarray)` An array of rectangular bounding boxes for detection boxes, with a shape of (n, 4) and dtype int16. Each row represents the [x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max] coordinates of a rectangle, where (x_min, y_min) is the top-left corner and (x_max, y_max) is the bottom-right corner
- Calling the `save_to_json()` method will save the above content to the specified `save_path`. If a directory is specified, the saved path will be `save_path/{your_img_basename}.json`. If a file is specified, it will be saved directly to that file. Since JSON files do not support saving numpy arrays, the `numpy.array` type will be converted to a list format.
- Calling the `save_to_img()` method will save the visualization results to the specified `save_path`. If a directory is specified, the saved path will be `save_path/{your_img_basename}_ocr_res_img.{your_img_extension}`. If a file is specified, it will be saved directly to that file. (Since the production line usually contains multiple result images, it is not recommended to specify a specific file path directly, as multiple images will be overwritten and only the last image will be retained)
* Additionally, it also supports obtaining the visualization image with results and the prediction results through attributes, as follows:
API Reference
For primary operations provided by the service:
- The HTTP request method is POST.
- Both the request body and response body are JSON data (JSON objects).
- When the request is processed successfully, the response status code is
200, and the properties of the response body are as follows:
| Name |
Type |
Meaning |
logId |
string |
The UUID of the request. |
errorCode |
integer |
Error code. Fixed as 0. |
errorMsg |
string |
Error message. Fixed as "Success". |
result |
object |
The result of the operation. |
- When the request is not processed successfully, the properties of the response body are as follows:
| Name |
Type |
Meaning |
logId |
string |
The UUID of the request. |
errorCode |
integer |
Error code. Same as the response status code. |
errorMsg |
string |
Error message. |
Primary operations provided by the service:
Get the OCR result of an image.
POST /ocr
- The properties of the request body are as follows:
| Name |
Type |
Meaning |
Required |
file |
string |
The URL of an image file or PDF file accessible by the server, or the Base64 encoded result of the content of the above-mentioned file types. For PDF files with more than 10 pages, only the content of the first 10 pages will be used. |
Yes |
fileType |
integer |
File type. 0 indicates a PDF file, and 1 indicates an image file. If this property is not present in the request body, the file type will be inferred based on the URL. |
No |
inferenceParams |
object |
Inference parameters. |
No |
The properties of inferenceParams are as follows:
| Name |
Type |
Meaning |
Required |
maxLongSide |
integer |
If the longer side of the input image for the text detection model exceeds maxLongSide during inference, the image will be scaled down so that its longer side equals maxLongSide. |
No |
- When the request is processed successfully, the
result in the response body has the following properties:
| Name |
Type |
Meaning |
ocrResults |
array |
OCR results. The array length is 1 (for image input) or the smaller of the number of document pages and 10 (for PDF input). For PDF input, each element in the array represents the processing result of each page in the PDF file. |
dataInfo |
object |
Information about the input data. |
Each element in ocrResults is an object with the following properties:
| Name |
Type |
Description |
texts |
array |
Text locations, content, and scores. |
image |
string |
The OCR result image with annotated text locations. The image is in JPEG format and Base64-encoded. |
Each element in texts is an object with the following properties:
| Name |
Type |
Meaning |
poly |
array |
Text location. The elements in the array are the coordinates of the vertices of the polygon surrounding the text. |
text |
string |
Text content. |
score |
number |
Text recognition score. |
Multi-language Service Call Examples
Python
import base64
import requests
API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/ocr"
file_path = "./demo.jpg"
with open(file_path, "rb") as file:
file_bytes = file.read()
file_data = base64.b64encode(file_bytes).decode("ascii")
payload = {"file": file_data, "fileType": 1}
# Call the API
response = requests.post(API_URL, json=payload)
# Process the response data
assert response.status_code == 200
result = response.json()["result"]
for i, res in enumerate(result["ocrResults"]):
print("Detected texts:")
print(res["texts"])
output_img_path = f"out_{i}.jpg"
with open(output_img_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(base64.b64decode(res["image"]))
print(f"Output image saved at {output_img_path}")
📱 Edge Deployment: Edge deployment is a method of placing computing and data processing capabilities directly on user devices, allowing them to process data locally without relying on remote servers. PaddleX supports deploying models on edge devices such as Android. For detailed instructions, please refer to the [PaddleX Edge Deployment Guide](../../../pipeline_deploy/edge_deploy.en.md).
You can choose the appropriate deployment method based on your needs to integrate the model production line into your AI applications.
## 4. Secondary Development
If the default model weights provided by the General OCR production line do not meet your requirements in terms of accuracy or speed, you can attempt to fine-tune the existing models using your own domain-specific or application-specific data to improve the recognition performance of the General OCR production line in your scenario.
### 4.1 Model Fine-Tuning
Since the General OCR production line consists of several modules, the unsatisfactory performance of the production line may originate from any one of these modules. You can analyze the images with poor recognition results to identify which module is problematic and refer to the corresponding fine-tuning tutorial links in the table below for model fine-tuning.
| Scenario |
Fine-Tuning Module |
Fine-Tuning Reference Link |
| Text is missed in detection |
Text Detection Module |
Link |
| Text content is inaccurate |
Text Recognition Module |
Link |
| Vertical or rotated text line correction is inaccurate |
Text Line Orientation Classification Module |
Link |
| Whole-image rotation correction is inaccurate |
Document Image Orientation Classification Module |
Link |
| Image distortion correction is inaccurate |
Text Image Correction Module |
Fine-tuning not supported yet |
### 4.2 Model Application
After fine-tuning with your private dataset, you will obtain the local model weight files.
If you need to use the fine-tuned model weights, simply modify the production line configuration file by replacing the local paths of the fine-tuned model weights into the corresponding positions in the configuration file:
```yaml
SubPipelines:
DocPreprocessor:
...
SubModules:
DocOrientationClassify:
module_name: doc_text_orientation
model_name: PP-LCNet_x1_0_doc_ori
model_dir: null # 替换为微调后的文档图像方向分类模型权重路径
...
SubModules:
TextDetection:
module_name: text_detection
model_name: PP-OCRv4_mobile_det
model_dir: null # 替换为微调后的文本检测模型权重路径
...
TextLineOrientation:
module_name: textline_orientation
model_name: PP-LCNet_x0_25_textline_ori
model_dir: null # 替换为微调后的文本行方向分类模型权重路径
batch_size: 1
TextRecognition:
module_name: text_recognition
model_name: PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec
model_dir: null # 替换为微调后的文本识别模型权重路径
batch_size: 1
```
Subsequently, refer to the command-line or Python script methods in [2.2 Local Experience](#22-local-experience) to load the modified production line configuration file.
## 5. Multi-Hardware Support
PaddleX supports a variety of mainstream hardware devices, including NVIDIA GPUs, Kunlunxin XPUs, Ascend NPUs, and Cambricon MLUs. Simply modify the `--device` parameter to seamlessly switch between different hardware devices.
For example, if you are using an NVIDIA GPU for OCR production line inference, the Python command is:
```bash
paddlex --pipeline OCR \
--input general_ocr_002.png \
--use_doc_orientation_classify False \
--use_doc_unwarping False \
--use_textline_orientation False \
--save_path ./output \
--device npu:0
```
If you want to use the General OCR production line on more types of hardware, please refer to the [PaddleX Multi-Hardware Usage Guide](../../../other_devices_support/multi_devices_use_guide.en.md).
 The General OCR production line includes mandatory text detection and text recognition modules, as well as optional document image orientation classification, text image correction, and text line orientation classification modules. The document image orientation classification and text image correction modules are integrated as a document preprocessing sub-line into the General OCR production line. Each module contains multiple models, and you can choose the model based on the benchmark test data below.
If you prioritize model accuracy, choose a high-accuracy model; if you prioritize inference speed, choose a faster inference model; if you care about model storage size, choose a smaller model.
The General OCR production line includes mandatory text detection and text recognition modules, as well as optional document image orientation classification, text image correction, and text line orientation classification modules. The document image orientation classification and text image correction modules are integrated as a document preprocessing sub-line into the General OCR production line. Each module contains multiple models, and you can choose the model based on the benchmark test data below.
If you prioritize model accuracy, choose a high-accuracy model; if you prioritize inference speed, choose a faster inference model; if you care about model storage size, choose a smaller model.
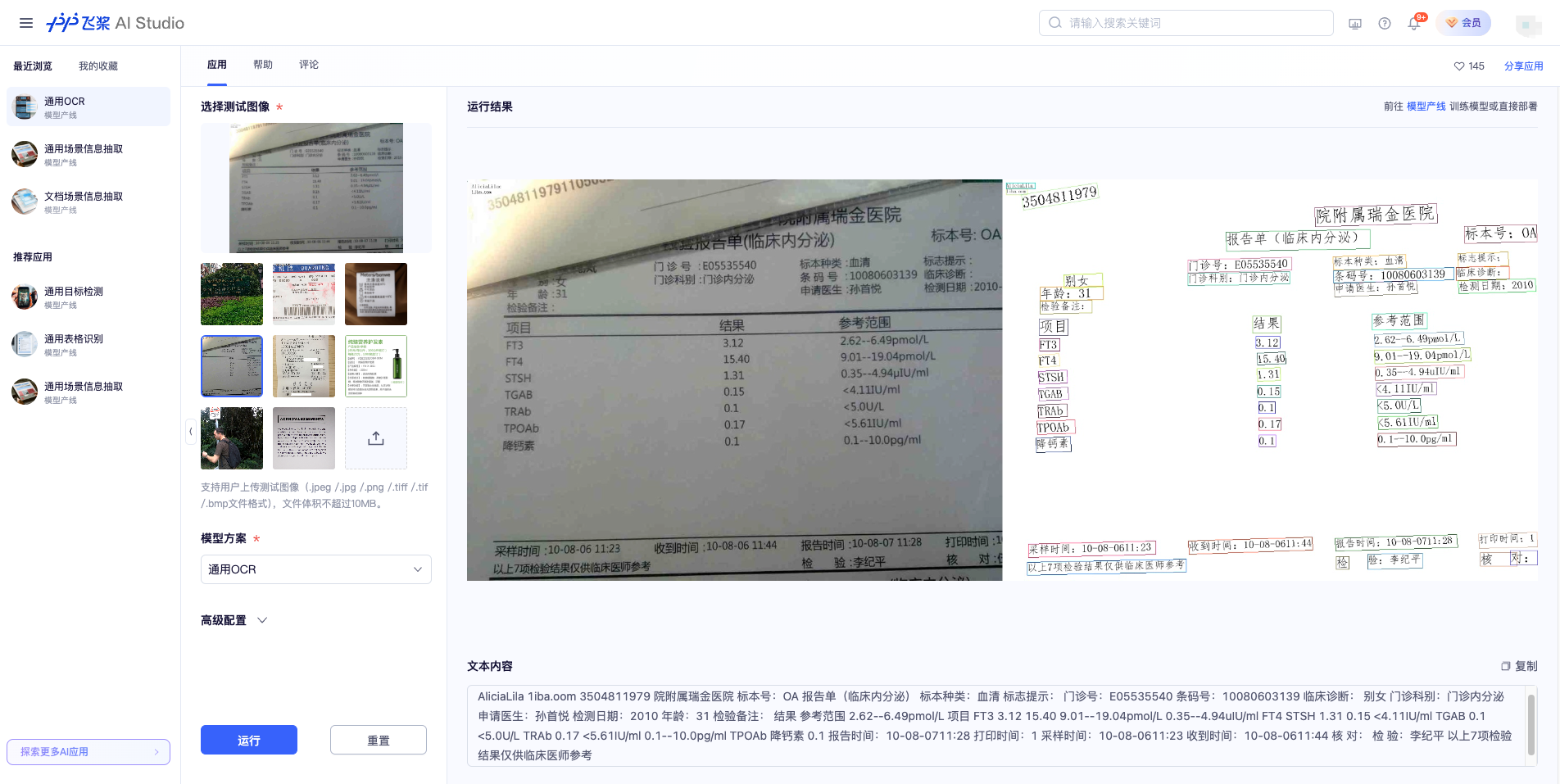 If you are satisfied with the performance of the production line, you can directly integrate and deploy it. You can choose to download the deployment package from the cloud, or refer to the methods in [Section 2.2 Local Experience](#22-local-experience) for local deployment. If you are not satisfied with the effect, you can fine-tune the models in the production line using your private data. If you have local hardware resources for training, you can start training directly on your local machine; if not, the Star River Zero-Code platform provides a one-click training service. You don't need to write any code—just upload your data and start the training task with one click.
### 2.2 Local Experience
> ❗ Before using the general OCR production line locally, please ensure that you have completed the installation of the PaddleX wheel package according to the [PaddleX Installation Guide](../../../installation/installation.en.md).
#### 2.2.1 Command Line Experience
* You can quickly experience the OCR production line with a single command. Use the [test image](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/general_ocr_002.png), and replace `--input` with the local path for prediction.
```bash
paddlex --pipeline OCR \
--input general_ocr_002.png \
--use_doc_orientation_classify False \
--use_doc_unwarping False \
--use_textline_orientation False \
--save_path ./output \
--device gpu:0
```
For details on the relevant parameter descriptions, please refer to the parameter descriptions in [2.2.2 Python Script Integration](#222-python-script-integration).
After running, the results will be printed to the terminal as follows:
```bash
{'res': {'input_path': 'general_ocr_002.png', 'model_settings': {'use_doc_preprocessor': False, 'use_textline_orientation': False}, 'doc_preprocessor_res': {'input_path': '0.jpg', 'model_settings': {'use_doc_orientation_classify': True, 'use_doc_unwarping': False}, 'angle': 0},'dt_polys': [array([[ 3, 10],
[82, 10],
[82, 33],
[ 3, 33]], dtype=int16), ...], 'text_det_params': {'limit_side_len': 960, 'limit_type': 'max', 'thresh': 0.3, 'box_thresh': 0.6, 'unclip_ratio': 2.0}, 'text_type': 'general', 'textline_orientation_angles': [-1, ...], 'text_rec_score_thresh': 0.0, 'rec_texts': ['www.99*', ...], 'rec_scores': [0.8980069160461426, ...], 'rec_polys': [array([[ 3, 10],
[82, 10],
[82, 33],
[ 3, 33]], dtype=int16), ...], 'rec_boxes': array([[ 3, 10, 82, 33], ...], dtype=int16)}}
```
The visualized results are saved under `save_path`, and the OCR visualization results are as follows:
If you are satisfied with the performance of the production line, you can directly integrate and deploy it. You can choose to download the deployment package from the cloud, or refer to the methods in [Section 2.2 Local Experience](#22-local-experience) for local deployment. If you are not satisfied with the effect, you can fine-tune the models in the production line using your private data. If you have local hardware resources for training, you can start training directly on your local machine; if not, the Star River Zero-Code platform provides a one-click training service. You don't need to write any code—just upload your data and start the training task with one click.
### 2.2 Local Experience
> ❗ Before using the general OCR production line locally, please ensure that you have completed the installation of the PaddleX wheel package according to the [PaddleX Installation Guide](../../../installation/installation.en.md).
#### 2.2.1 Command Line Experience
* You can quickly experience the OCR production line with a single command. Use the [test image](https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/general_ocr_002.png), and replace `--input` with the local path for prediction.
```bash
paddlex --pipeline OCR \
--input general_ocr_002.png \
--use_doc_orientation_classify False \
--use_doc_unwarping False \
--use_textline_orientation False \
--save_path ./output \
--device gpu:0
```
For details on the relevant parameter descriptions, please refer to the parameter descriptions in [2.2.2 Python Script Integration](#222-python-script-integration).
After running, the results will be printed to the terminal as follows:
```bash
{'res': {'input_path': 'general_ocr_002.png', 'model_settings': {'use_doc_preprocessor': False, 'use_textline_orientation': False}, 'doc_preprocessor_res': {'input_path': '0.jpg', 'model_settings': {'use_doc_orientation_classify': True, 'use_doc_unwarping': False}, 'angle': 0},'dt_polys': [array([[ 3, 10],
[82, 10],
[82, 33],
[ 3, 33]], dtype=int16), ...], 'text_det_params': {'limit_side_len': 960, 'limit_type': 'max', 'thresh': 0.3, 'box_thresh': 0.6, 'unclip_ratio': 2.0}, 'text_type': 'general', 'textline_orientation_angles': [-1, ...], 'text_rec_score_thresh': 0.0, 'rec_texts': ['www.99*', ...], 'rec_scores': [0.8980069160461426, ...], 'rec_polys': [array([[ 3, 10],
[82, 10],
[82, 33],
[ 3, 33]], dtype=int16), ...], 'rec_boxes': array([[ 3, 10, 82, 33], ...], dtype=int16)}}
```
The visualized results are saved under `save_path`, and the OCR visualization results are as follows:
 #### 2.2.2 Python Script Integration
* The above command line is for quick experience and effect checking. Generally, in a project, integration through code is often required. You can complete the quick inference of the production line with just a few lines of code. The inference code is as follows:
```python
from paddlex import create_pipeline
pipeline = create_pipeline(pipeline="OCR")
output = pipeline.predict(
input="./general_ocr_002.png",
use_doc_orientation_classify=False,
use_doc_unwarping=False,
use_textline_orientation=False,
)
for res in output:
res.print()
res.save_to_img(save_path="./output/")
res.save_to_json(save_path="./output/")
```
In the above Python script, the following steps are executed:
(1) The OCR production line object is instantiated via `create_pipeline()`, with specific parameter descriptions as follows:
#### 2.2.2 Python Script Integration
* The above command line is for quick experience and effect checking. Generally, in a project, integration through code is often required. You can complete the quick inference of the production line with just a few lines of code. The inference code is as follows:
```python
from paddlex import create_pipeline
pipeline = create_pipeline(pipeline="OCR")
output = pipeline.predict(
input="./general_ocr_002.png",
use_doc_orientation_classify=False,
use_doc_unwarping=False,
use_textline_orientation=False,
)
for res in output:
res.print()
res.save_to_img(save_path="./output/")
res.save_to_json(save_path="./output/")
```
In the above Python script, the following steps are executed:
(1) The OCR production line object is instantiated via `create_pipeline()`, with specific parameter descriptions as follows: