high_performance_inference.en.md 17 KB
comments: true
PaddleX High-Performance Inference Guide
In real-world production environments, many applications have stringent standards for deployment strategy performance metrics, particularly response speed, to ensure efficient system operation and smooth user experience. To this end, PaddleX provides high-performance inference plugins designed to deeply optimize model inference and pre/post-processing, achieving significant speedups in the end-to-end process. This document will first introduce the installation and usage of the high-performance inference plugins, followed by a list of pipelines and models currently supporting the use of these plugins.
1. Installation and Usage of High-Performance Inference Plugins
Before using the high-performance inference plugins, ensure you have completed the installation of PaddleX according to the PaddleX Local Installation Tutorial, and have successfully run the quick inference of the pipeline using either the PaddleX pipeline command line instructions or the Python script instructions.
1.1 Installing High-Performance Inference Plugins
Find the corresponding installation command based on your processor architecture, operating system, device type, and Python version in the table below and execute it in your deployment environment. Please replace {paddlex version number} with the actual paddlex version number, such as the current latest stable version 3.0.0b2. If you need to use the version corresponding to the development branch, replace {paddlex version number} with 0.0.0.dev0.
| Processor Architecture | Operating System | Device Type | Python Version | Installation Command |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x86-64 | Linux | CPU | ||
| 3.8 | curl -s https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/PaddleX3.0/deploy/paddlex_hpi/install_script/{paddlex version number}/install_paddlex_hpi.py | python3.8 - --arch x86_64 --os linux --device cpu --py 38 | |||
| 3.9 | curl -s https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/PaddleX3.0/deploy/paddlex_hpi/install_script/{paddlex version number}/install_paddlex_hpi.py | python3.9 - --arch x86_64 --os linux --device cpu --py 39 | |||
| 3.10 | curl -s https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/PaddleX3.0/deploy/paddlex_hpi/install_script/{paddlex version number}/install_paddlex_hpi.py | python3.10 - --arch x86_64 --os linux --device cpu --py 310 | |||
| GPU (CUDA 11.8 + cuDNN 8.6) | 3.8 | curl -s https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/PaddleX3.0/deploy/paddlex_hpi/install_script/{paddlex version number}/install_paddlex_hpi.py | python3.8 - --arch x86_64 --os linux --device gpu_cuda118_cudnn86 --py 38 | ||
| 3.9 | curl -s https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/PaddleX3.0/deploy/paddlex_hpi/install_script/{paddlex version number}/install_paddlex_hpi.py | python3.9 - --arch x86_64 --os linux --device gpu_cuda118_cudnn86 --py 39 | |||
| 3.10 | curl -s https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/PaddleX3.0/deploy/paddlex_hpi/install_script/{paddlex version number}/install_paddlex_hpi.py | python3.10 - --arch x86_64 --os linux --device gpu_cuda118_cudnn86 --py 310 |
- For Linux systems, execute the installation instructions using Bash.
- When using NVIDIA GPUs, please use the installation instructions corresponding to the CUDA and cuDNN versions that match your environment. Otherwise, you will not be able to use the high-performance inference plugin properly.
- When the device type is CPU, the installed high-performance inference plugin only supports inference using the CPU; for other device types, the installed high-performance inference plugin supports inference using the CPU or other devices.
1.2 Obtaining Serial Numbers and Activation
On the Baidu AIStudio Community - AI Learning and Training Platform page, under the "Open-source Pipeline Deployment Serial Number Inquiry and Acquisition" section, select "Acquire Now" as shown in the following image:
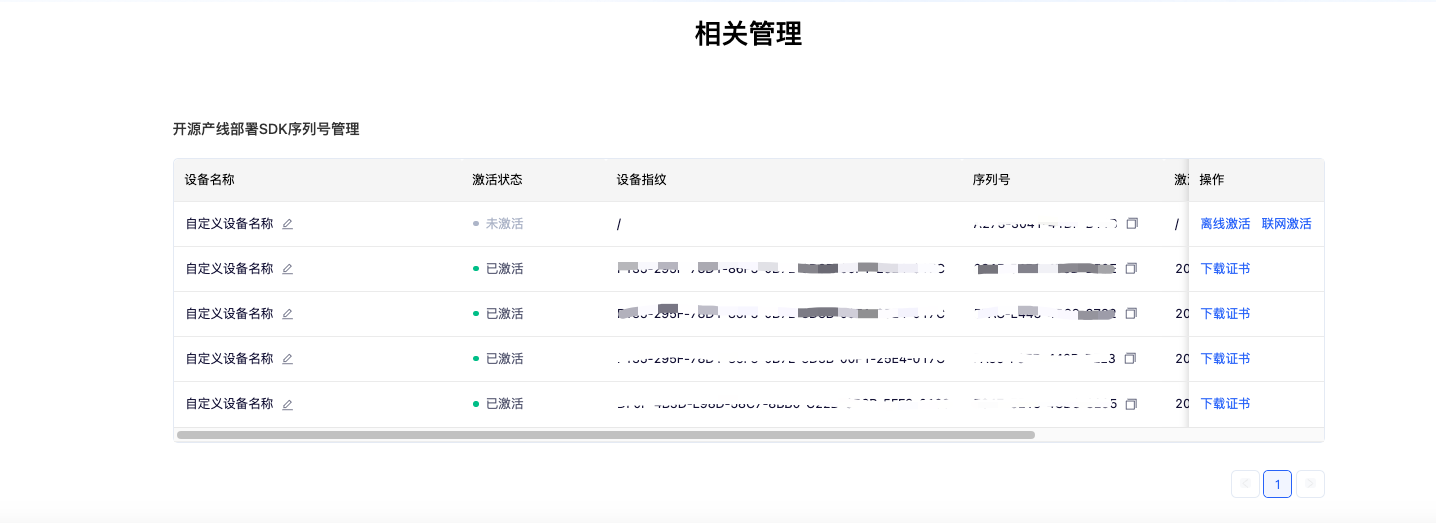
Select the pipeline you wish to deploy and click "Acquire". Afterwards, you can find the acquired serial number in the "Open-source Pipeline Deployment SDK Serial Number Management" section at the bottom of the page:
After using the serial number to complete activation, you can utilize high-performance inference plugins. PaddleX provides both online and offline activation methods (both only support Linux systems):
- Online Activation: When using the inference API or CLI, specify the serial number and enable online activation to automatically complete the process.
- Offline Activation: Follow the instructions in the serial number management interface (click "Offline Activation" under "Operations") to obtain the device fingerprint of your machine. Bind the serial number with the device fingerprint to obtain a certificate and complete the activation. For this activation method, you need to manually store the certificate in the
${HOME}/.baidu/paddlex/licensesdirectory on the machine (create the directory if it does not exist) and specify the serial number when using the inference API or CLI.
Please note: Each serial number can only be bound to a unique device fingerprint and can only be bound once. This means that if users deploy models on different machines, they must prepare separate serial numbers for each machine.
1.3 Enabling High-Performance Inference Plugins
For Linux systems, if using the high-performance inference plugin in a Docker container, please mount the host machine's /dev/disk/by-uuid and ${HOME}/.baidu/paddlex/licenses directories to the container.
For PaddleX CLI, specify --use_hpip and set the serial number to enable the high-performance inference plugin. If you wish to activate the license online, specify --update_license when using the serial number for the first time. Taking the general image classification pipeline as an example:
paddlex \
--pipeline image_classification \
--input https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/general_image_classification_001.jpg \
--device gpu:0 \
--use_hpip \
--serial_number {serial_number}
# If you wish to perform online activation
paddlex \
--pipeline image_classification \
--input https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/general_image_classification_001.jpg \
--device gpu:0 \
--use_hpip \
--serial_number {serial_number} \
--update_license
For PaddleX Python API, enabling the high-performance inference plugin is similar. Still taking the general image classification pipeline as an example:
from paddlex import create_pipeline
pipeline = create_pipeline(
pipeline="image_classification",
use_hpip=True,
hpi_params={"serial_number": "{serial_number}"},
)
output = pipeline.predict("https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/general_image_classification_001.jpg")
The inference results obtained with the high-performance inference plugin enabled are consistent with those without the plugin enabled. For some models, enabling the high-performance inference plugin for the first time may take a longer time to complete the construction of the inference engine. PaddleX will cache the relevant information in the model directory after the first construction of the inference engine and reuse the cached content in subsequent runs to improve initialization speed.
1.4 Modifying High-Performance Inference Configurations
PaddleX combines model information and runtime environment information to provide default high-performance inference configurations for each model. These default configurations are carefully prepared to be applicable in several common scenarios and achieve relatively optimal performance. Therefore, users typically may not need to be concerned with the specific details of these configurations. However, due to the diversity of actual deployment environments and requirements, the default configuration may not yield ideal performance in certain scenarios and could even result in inference failures. In cases where the default configuration does not meet the requirements, users can manually adjust the configuration by modifying the Hpi field in the inference.yml file within the model directory (if this field does not exist, it needs to be added). The following are two common situations:
Switching inference backends:
When the default inference backend is not available, the inference backend needs to be switched manually. Users should modify the
selected_backendsfield (if it does not exist, it needs to be added).Hpi: ... selected_backends: cpu: paddle_infer gpu: onnx_runtime ...Each entry should follow the format
{device type}: {inference backend name}.The currently available inference backends are:
paddle_infer: The Paddle Inference engine. Supports CPU and GPU. Compared to the PaddleX quick inference, TensorRT subgraphs can be integrated to enhance inference performance on GPUs.openvino: OpenVINO, a deep learning inference tool provided by Intel, optimized for model inference performance on various Intel hardware. Supports CPU only. The high-performance inference plugin automatically converts the model to the ONNX format and uses this engine for inference.onnx_runtime: ONNX Runtime, a cross-platform, high-performance inference engine. Supports CPU and GPU. The high-performance inference plugin automatically converts the model to the ONNX format and uses this engine for inference.tensorrt: TensorRT, a high-performance deep learning inference library provided by NVIDIA, optimized for NVIDIA GPUs to improve speed. Supports GPU only. The high-performance inference plugin automatically converts the model to the ONNX format and uses this engine for inference.
Modifying dynamic shape configurations for Paddle Inference or TensorRT:
Dynamic shape is the ability of TensorRT to defer specifying parts or all of a tensor’s dimensions until runtime. If the default dynamic shape configuration does not meet requirements (e.g., the model may require input shapes beyond the default range), users need to modify the
trt_dynamic_shapesordynamic_shapesfield in the inference backend configuration:Hpi: ... backend_configs: # Configuration for the Paddle Inference backend paddle_infer: ... trt_dynamic_shapes: x: - [1, 3, 300, 300] - [4, 3, 300, 300] - [32, 3, 1200, 1200] ... # Configuration for the TensorRT backend tensorrt: ... dynamic_shapes: x: - [1, 3, 300, 300] - [4, 3, 300, 300] - [32, 3, 1200, 1200] ...In
trt_dynamic_shapesordynamic_shapes, each input tensor requires a specified dynamic shape in the format:{input tensor name}: [{minimum shape}, [{optimal shape}], [{maximum shape}]]. For details on minimum, optimal, and maximum shapes and further information, please refer to the official TensorRT documentation.After completing the modifications, please delete the cache files in the model directory (
shape_range_info.pbtxtand files starting withtrt_serialized).
2. Pipelines and Models Supporting High-Performance Inference Plugins
| Pipeline | Pipeline Module | Specific Models |
|---|---|---|
| General Image Classification | Image Classification | ResNet18 ResNet34 moreResNet50ResNet101 ResNet152 ResNet18_vd ResNet34_vd ResNet50_vd ResNet101_vd ResNet152_vd ResNet200_vd PP-LCNet_x0_25 PP-LCNet_x0_35 PP-LCNet_x0_5 PP-LCNet_x0_75 PP-LCNet_x1_0 PP-LCNet_x1_5 PP-LCNet_x2_0 PP-LCNet_x2_5 PP-LCNetV2_small PP-LCNetV2_base PP-LCNetV2_large MobileNetV3_large_x0_35 MobileNetV3_large_x0_5 MobileNetV3_large_x0_75 MobileNetV3_large_x1_0 MobileNetV3_large_x1_25 MobileNetV3_small_x0_35 MobileNetV3_small_x0_5 MobileNetV3_small_x0_75 MobileNetV3_small_x1_0 MobileNetV3_small_x1_25 ConvNeXt_tiny ConvNeXt_small ConvNeXt_base_224 ConvNeXt_base_384 ConvNeXt_large_224 ConvNeXt_large_384 MobileNetV1_x0_25 MobileNetV1_x0_5 MobileNetV1_x0_75 MobileNetV1_x1_0 MobileNetV2_x0_25 MobileNetV2_x0_5 MobileNetV2_x1_0 MobileNetV2_x1_5 MobileNetV2_x2_0 SwinTransformer_tiny_patch4_window7_224 SwinTransformer_small_patch4_window7_224 SwinTransformer_base_patch4_window7_224 SwinTransformer_base_patch4_window12_384 SwinTransformer_large_patch4_window7_224 SwinTransformer_large_patch4_window12_384 PP-HGNet_small PP-HGNet_tiny PP-HGNet_base PP-HGNetV2-B0 PP-HGNetV2-B1 PP-HGNetV2-B2 PP-HGNetV2-B3 PP-HGNetV2-B4 PP-HGNetV2-B5 PP-HGNetV2-B6 CLIP_vit_base_patch16_224 CLIP_vit_large_patch14_224 |
| General Object Detection | Object Detection | PP-YOLOE_plus-S PP-YOLOE_plus-M morePP-YOLOE_plus-LPP-YOLOE_plus-X YOLOX-N YOLOX-T YOLOX-S YOLOX-M YOLOX-L YOLOX-X YOLOv3-DarkNet53 YOLOv3-ResNet50_vd_DCN YOLOv3-MobileNetV3 RT-DETR-R18 RT-DETR-R50 RT-DETR-L RT-DETR-H RT-DETR-X PicoDet-S PicoDet-L |
| General Semantic Segmentation | Semantic Segmentation | Deeplabv3-R50 Deeplabv3-R101 moreDeeplabv3_Plus-R50Deeplabv3_Plus-R101 PP-LiteSeg-T OCRNet_HRNet-W48 OCRNet_HRNet-W18 SeaFormer_tiny SeaFormer_small SeaFormer_base SeaFormer_large SegFormer-B0 SegFormer-B1 SegFormer-B2 SegFormer-B3 SegFormer-B4 SegFormer-B5 |
| General Instance Segmentation | Instance Segmentation | Mask-RT-DETR-L Mask-RT-DETR-H |
| Seal Text Recognition | Layout Analysis | PicoDet-S_layout_3cls PicoDet-S_layout_17cls morePicoDet-L_layout_3clsPicoDet-L_layout_17cls RT-DETR-H_layout_3cls RT-DETR-H_layout_17cls |
| Seal Text Detection | PP-OCRv4_server_seal_det PP-OCRv4_mobile_seal_det |
|
| Text Recognition | PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec PP-OCRv4_server_rec |
|
| General OCR | Text Detection | PP-OCRv4_server_det PP-OCRv4_mobile_det |
| Text Recognition | PP-OCRv4_server_rec PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec ch_RepSVTR_rec ch_SVTRv2_rec |
|
| General Table Recognition | Layout Detection | PicoDet_layout_1x |
| Table Recognition | SLANet | |
| SLANet_plus | ||
| Text Detection | PP-OCRv4_server_det PP-OCRv4_mobile_det |
|
| Text Recognition | PP-OCRv4_server_rec PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec ch_RepSVTR_rec ch_SVTRv2_rec |
|
| Document Scene Information Extraction v3 | Table Recognition | SLANet |
| SLANet_plus | ||
| Layout Detection | PicoDet_layout_1x | |
| Text Detection | PP-OCRv4_server_det | |
| PP-OCRv4_mobile_det | ||
| Text Recognition | PP-OCRv4_server_rec | |
| PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec | ||
| ch_RepSVTR_rec | ||
| ch_SVTRv2_rec | ||
| Seal Text Detection | PP-OCRv4_server_seal_det | |
| PP-OCRv4_mobile_seal_det | ||
| Text Image Rectification | UVDoc | |
| Document Image Orientation Classification | PP-LCNet_x1_0_doc_ori |